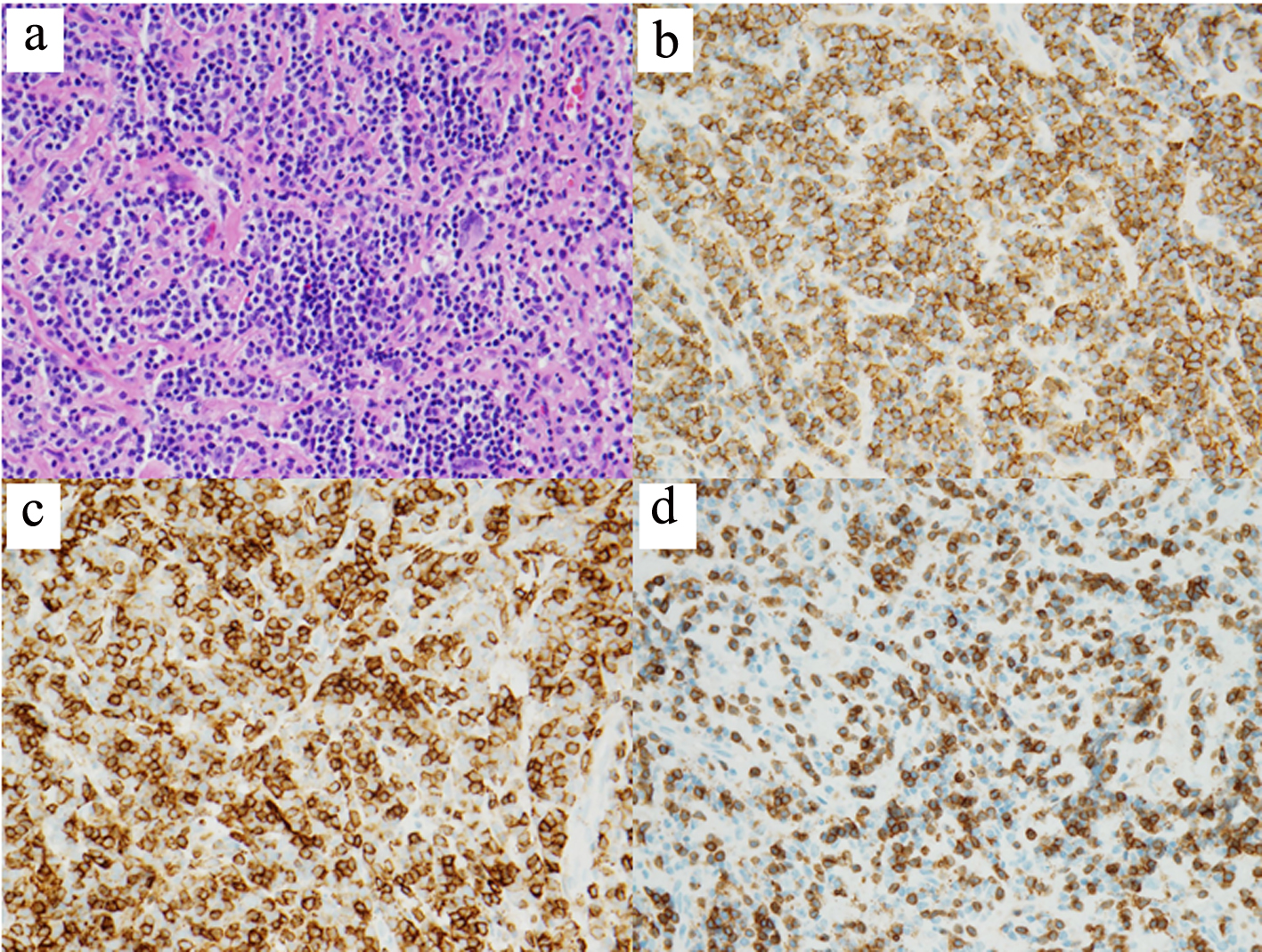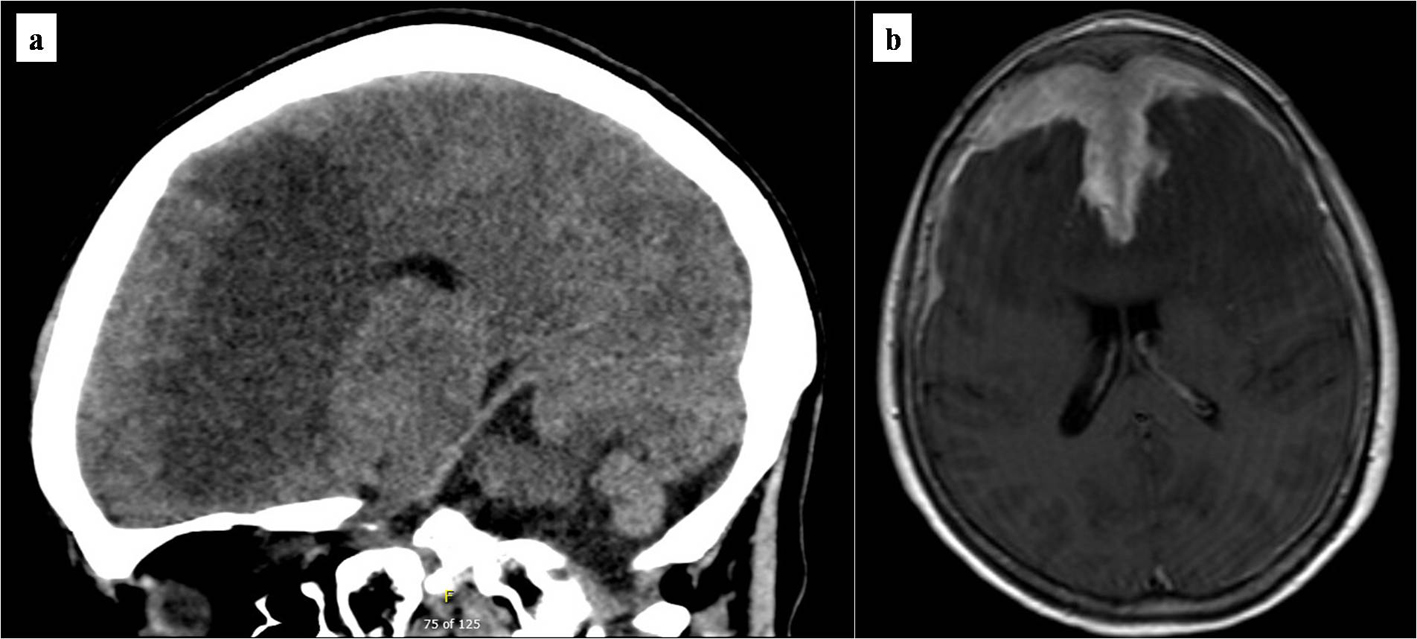
Figure 1. Brain imaging at presentation. (a) Initial non-contrasted computed tomography scan of the brain. Marked bifrontal white matter hypodensity extends across the corpus callosum with mass effect on the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles. In addition, there is a large poorly marginated region of hyperdensity along the anterior falx and anterior cranial vault which appears extra-axial. (b) T1/2-weighted brain MRI. Bifrontal extra-axial mass with extensive dural tail with invasion into both frontal lobes and extensive edema extending across the corpus callosum. MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.