Figures
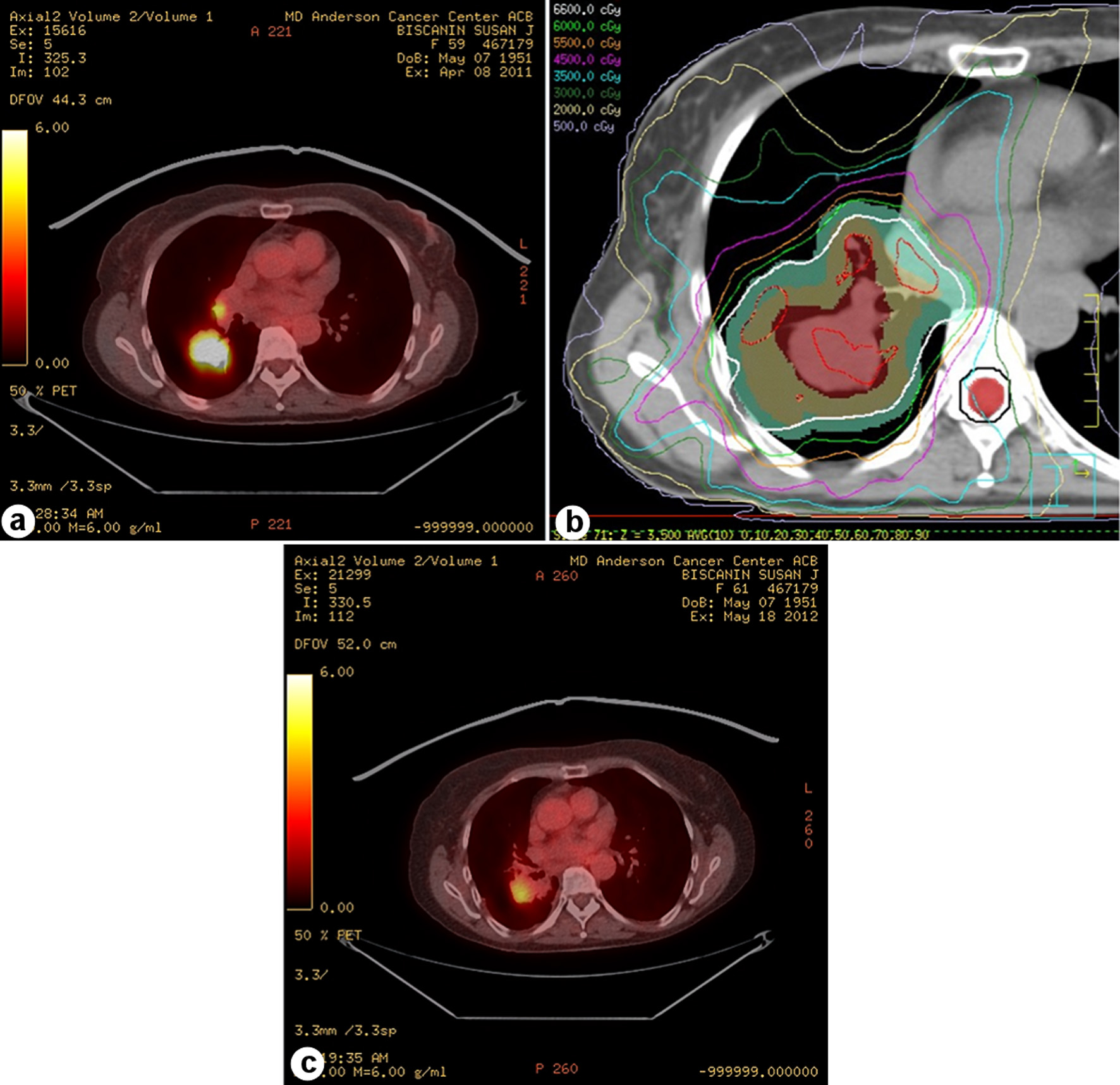
Figure 1. Local tumor progression in a patient with stage III adenocarcinoma lung cancer. (a) Positron emission tomography (PET) image from diagnosis. (b) Intensity-modulated photon radiation therapy plan with isodose lines and planning target volume (PTV) in green colorwash. (c) Post-treatment PET scan shows local tumor progression inside the PTV.
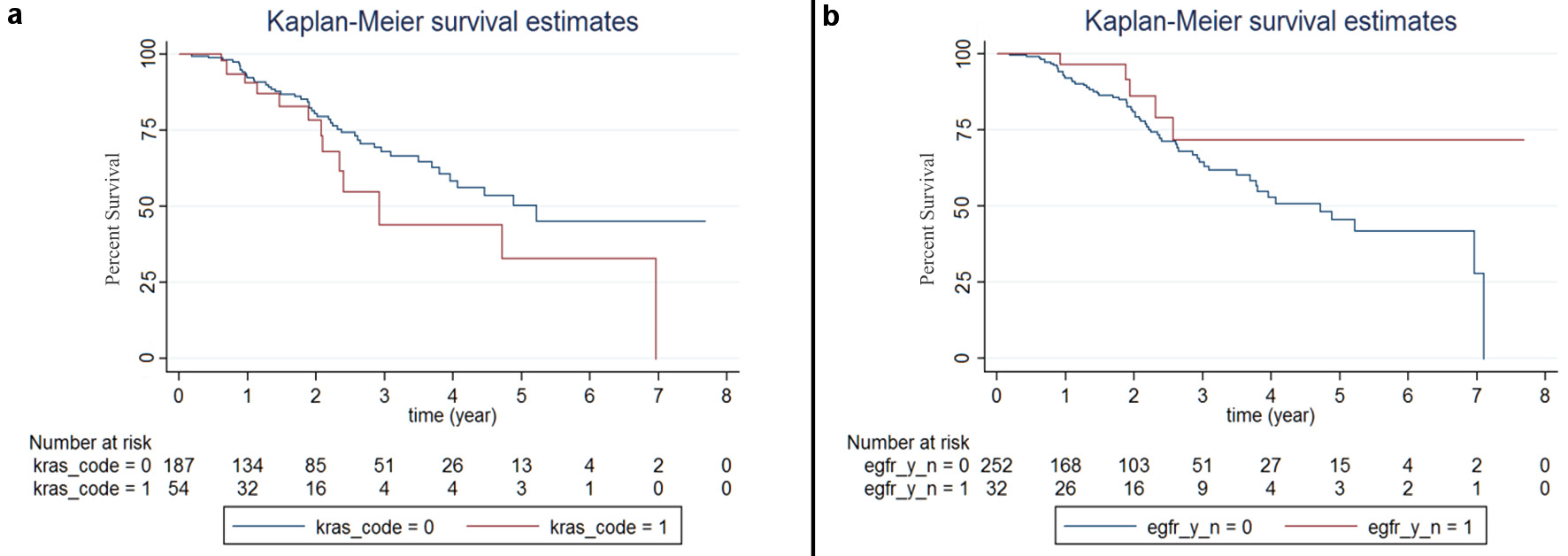
Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier plots of local progression-free survival (LPFS) according to EGFR and KRAS mutation status. (a) LPFS curves for patients with KRAS mutation (red line; krasm = 1), KRAS wild-type (WT; blue line (krasm = 0), P = 0.129). (b) LPFS curves for patients with EGFR mutation (red line; egfr = 1), EGFR WT (blue line; egfr = 0) P = 0.099. EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; KRAS: V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog.
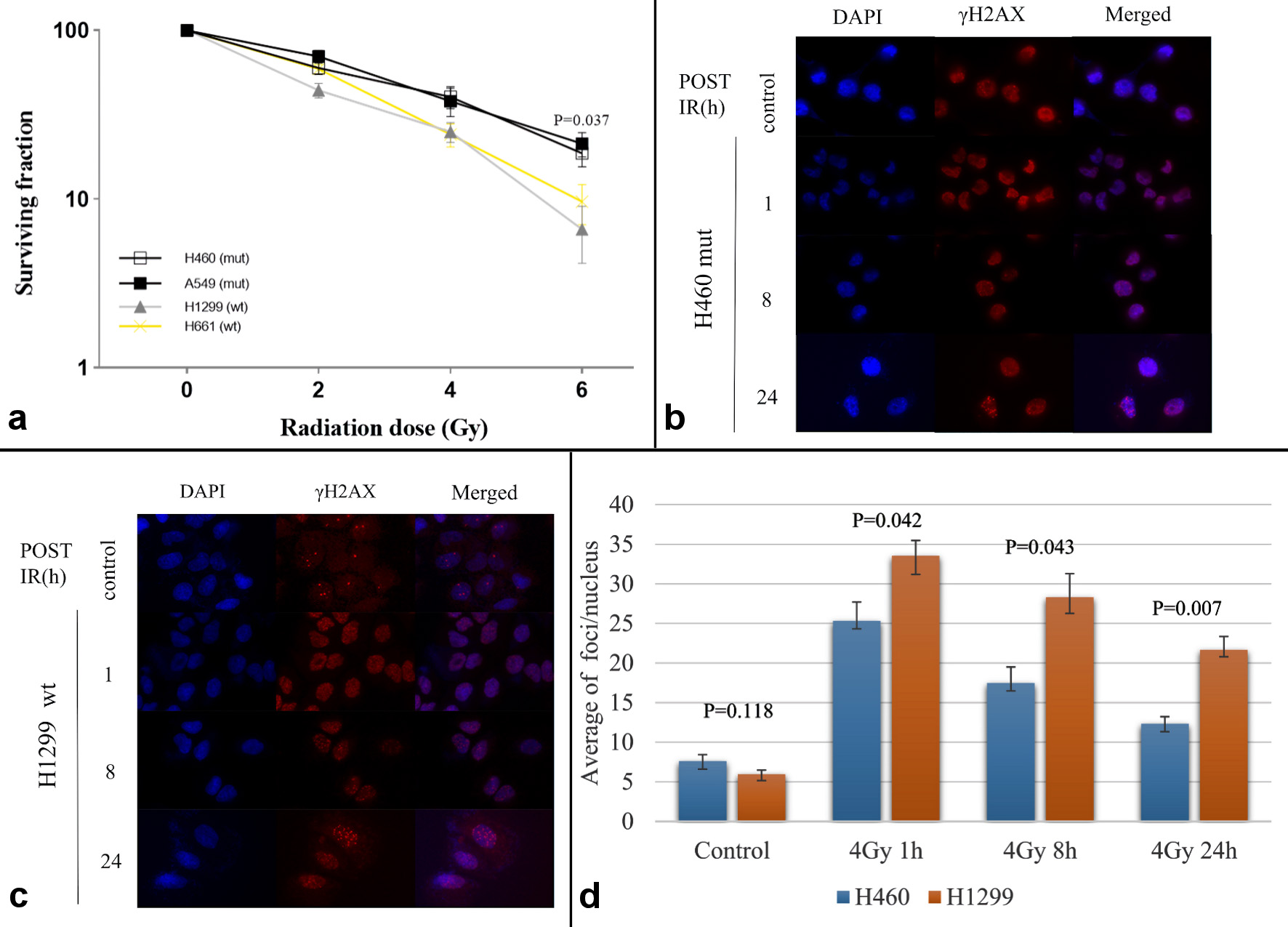
Figure 3. (a) Clonogenic assays showed that cell lines with KRAS mutation (H460 and A549) are more resistant than wild-type cells (H1299 and H661) to radiation. (b) H460 (KRAS mutation) and (c) H1299 (KRAS wild-type) treated with 4 Gy X-ray for 1, 8, and 24 h. Cells were then fixed and immune stained for γH2AX foci (red). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). (d) For each time point, five to 10 images were captured and used for quantification of γH2AX foci number. The graph represents an average of three independent experiments ± SD. KRAS: V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; SD: standard deviation.
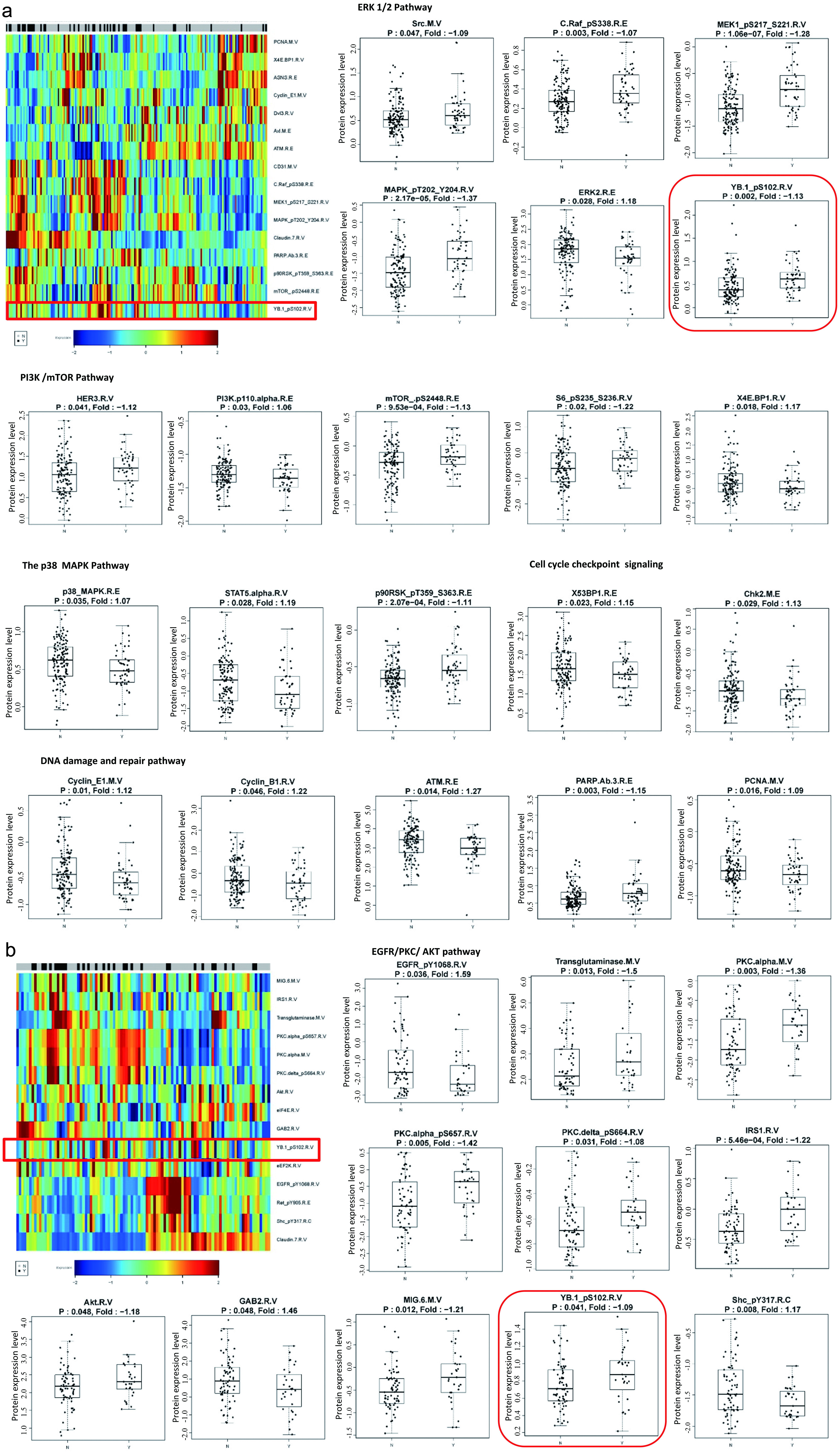
Figure 4. TCGA LUAD data show differentially expressed genes in the ERK1/2 pathway, phosphatidylinositol I3 kinase (PI3K)/mTOR, p38 MAPK pathway, cell cycle checkpoint signaling, and DNA damage. The repair and EGFR/PKC/AKT pathways presented with differential expression in patients (a) and cell lines (b) with KRAS mutations compared with the wild-type group. Y: patients or cell line with mutation; N: patients or cell line without mutation. TCGA LUAD: The Cancer Genome Atlas for Lung Adenocarcinoma.
Tables
Table 1. Patient Characteristics
| Characteristic | All | Local progression | No local progression | P value |
|---|
| EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; KRAS: V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; WT: wild-type; NSCLC: non-small cell lung cancer. |
| KRAS status | | | | |
| WT | 187 | 46 | 141 | 0.843 |
| Mutation | 54 | 14 | 40 | |
| EGFR status | | | | |
| WT | 252 | 62 | 190 | 0.376 |
| Mutation | 32 | 5 | 27 | |
| Age, years, mean ± SD | 63.9 ± 10.4 | 61.9 ± 9.7 | 64.6 ± 10.6 | 0.034 |
| Sex | | | | |
| Male | 144 | 38 | 106 | 0.296 |
| Female | 142 | 30 | 112 | |
| Race | | | | |
| Other | 31 | 9 | 22 | 0.467 |
| White | 255 | 59 | 196 | |
| Karnofsky performance status | | | | |
| > 80 | 120 | 26 | 94 | 0.476 |
| ≤ 80 | 166 | 42 | 124 | |
| Disease stage | | | | |
| I - II | 34 | 9 | 25 | 0.694 |
| III | 252 | 59 | 193 | |
| Tumor histology | | | | |
| Squamous cell | 67 | 21 | 46 | 0.122 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 177 | 35 | 142 | |
| NSCLC, other | 42 | 12 | 30 | |
| Smoking status | | | | |
| No smoking | 42 | 11 | 31 | 0.242 |
| Former | 178 | 37 | 141 | |
| Current | 61 | 19 | 42 | |
| Dose, mean ± SD, Gy or Gy (RBE) | 68.7 ± 6.2 | 68.1 ± 5.1 | 68.7 ± 6.5 | 0.785 |
| Radiation modality | | | | |
| Photon | 173 | 50 | 123 | 0.012 |
| Proton | 113 | 18 | 95 | |
| Chemotherapy | | | | |
| No induction chemotherapy | 185 | 36 | 149 | 0.02 |
| Induction chemotherapy | 101 | 32 | 69 | |
| No concurrent chemotherapy | 24 | 8 | 16 | 0.251 |
| Concurrent chemo | 262 | 60 | 202 | |
| Gross tumor volume, cm3 | 122.0 ± 128.1 | 120.2 ± 120.5 | 122.5 ± 130.7 | 0.852 |
Table 2. Univariate Analysis of Independent Predictors of Local Progression
| HR | 95% CI | P value |
|---|
| EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; KRAS: V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; WT: wild-type; NSCLC: non-small cell lung cancer; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval. |
| KRAS status | | | |
| WT (reference) | | | |
| Mutation | 1.585 | 0.865 - 2.901 | 0.135 |
| EGFR status | | | |
| WT (reference) | | | |
| Mutation | 0.475 | 0.190 - 1.119 | 0.113 |
| Age, years | 0.986 | 0.961 - 1.012 | 0.301 |
| Sex | | | |
| Male (reference) | | | |
| Female | 0.754 | 0.462 - 1.229 | 0.258 |
| Race | | | |
| Non-white (reference) | | | |
| White | 0.97 | 0.479 - 1.96 | 0.933 |
| Karnofsky performance status | | | |
| > 80 (reference) | | | |
| ≤ 80 | 1.149 | 0.698 - 1.891 | 0.585 |
| Disease stage | | | |
| I - II (reference) | | | |
| III | 0.966 | 0.476 - 1.957 | 0.923 |
| Tumor histology | | | |
| Squamous cell (reference) | | | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 0.783 | 0.452 - 1.355 | 0.382 |
| NSCLC, other | 0.78 | 0.383 - 1.588 | 0.494 |
| Smoking status | | | |
| No smoking (reference) | | | |
| Former | 0.886 | 0.449 - 1.748 | 0.727 |
| Current | 1.217 | 0.578 - 2.564 | 0.605 |
| Radiation dose, Gy or Gy (RBE) | 1.012 | 0.969 - 1.057 | 0.574 |
| Radiation modality | | | |
| Photon (reference) | | | |
| Proton | 0.772 | 0.449 - 1.326 | 0.348 |
| Chemotherapy | | | |
| No induction chemotherapy (reference) | | | |
| Induction chemotherapy | 1.091 | 0.673 - 1.768 | 0.724 |
| No concurrent chemotherapy (reference) | | | |
| Concurrent chemotherapy | 0.385 | 0.182 - 0.815 | 0.013 |
| Gross tumor volume, cm3 | 1.002 | 0.999 - 1.004 | 0.058 |
Table 3. Multivariate Analysis of Independent Predictors of Local Progression
| KRAS status | EGFR status |
|---|
| HR (95% CI) | P value | HR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|
| EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; KRAS: V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; WT: wild-type; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval. |
| KRAS status | | | | |
| WT (reference) | 1.961 (1.062 - 3.622) | 0.031 | | |
| Mutation | | | | |
| EGFR status | | | | |
| WT (reference) | | | 0.601 (0.237 - 1.52) | 0.283 |
| Mutation | | | | |
| Chemotherapy | | | | |
| No concurrent chemotherapy (reference) | 0.301 (0.132 - 0.683) | 0.004 | 0.352 (0.156 - 0.798) | 0.012 |
| Concurrent chemotherapy | | | | |
| Gross tumor volume, cm3 | 1.003 (1.000 - 1.004) | 0.013 | 1.002 (1.000 - 1.005) | 0.017 |



