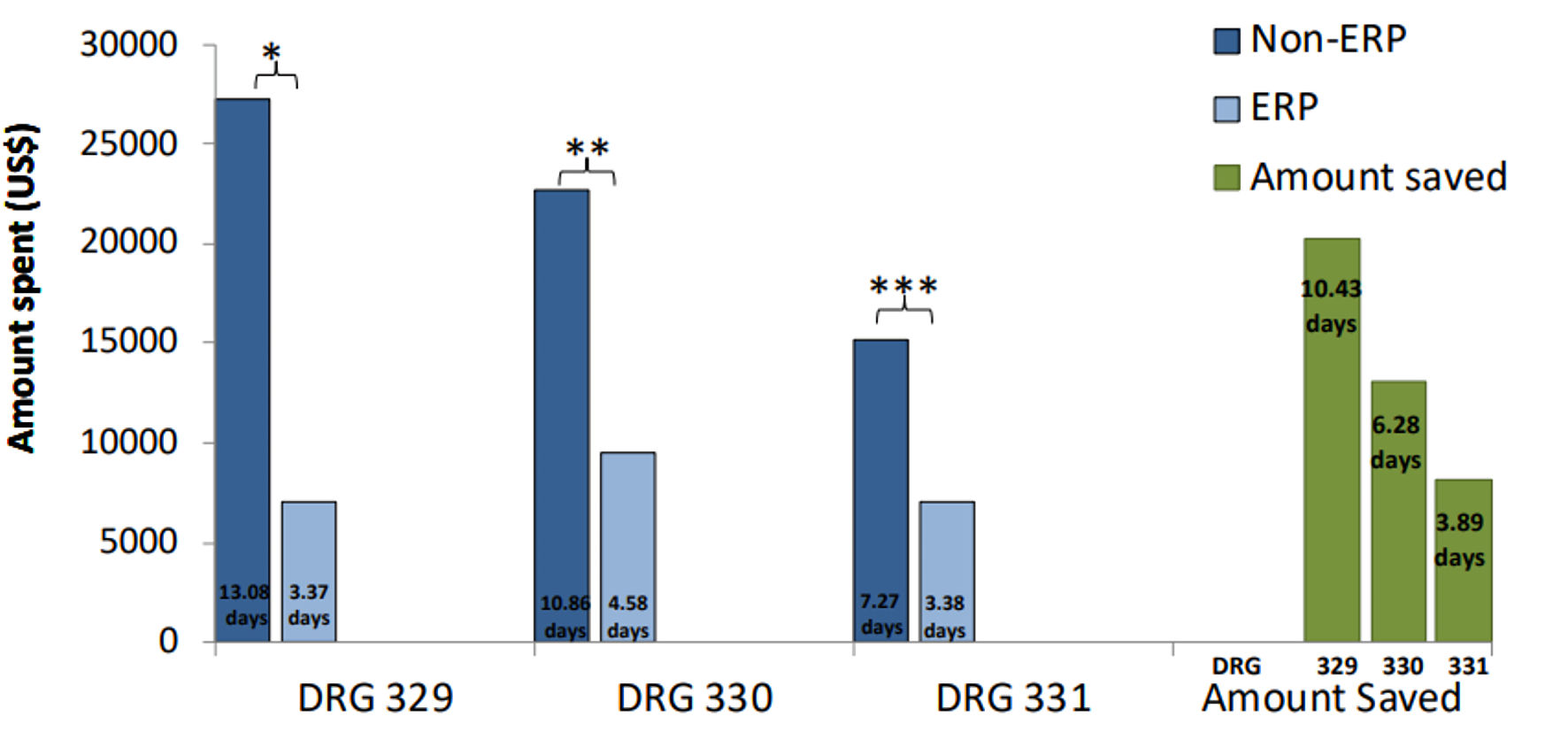
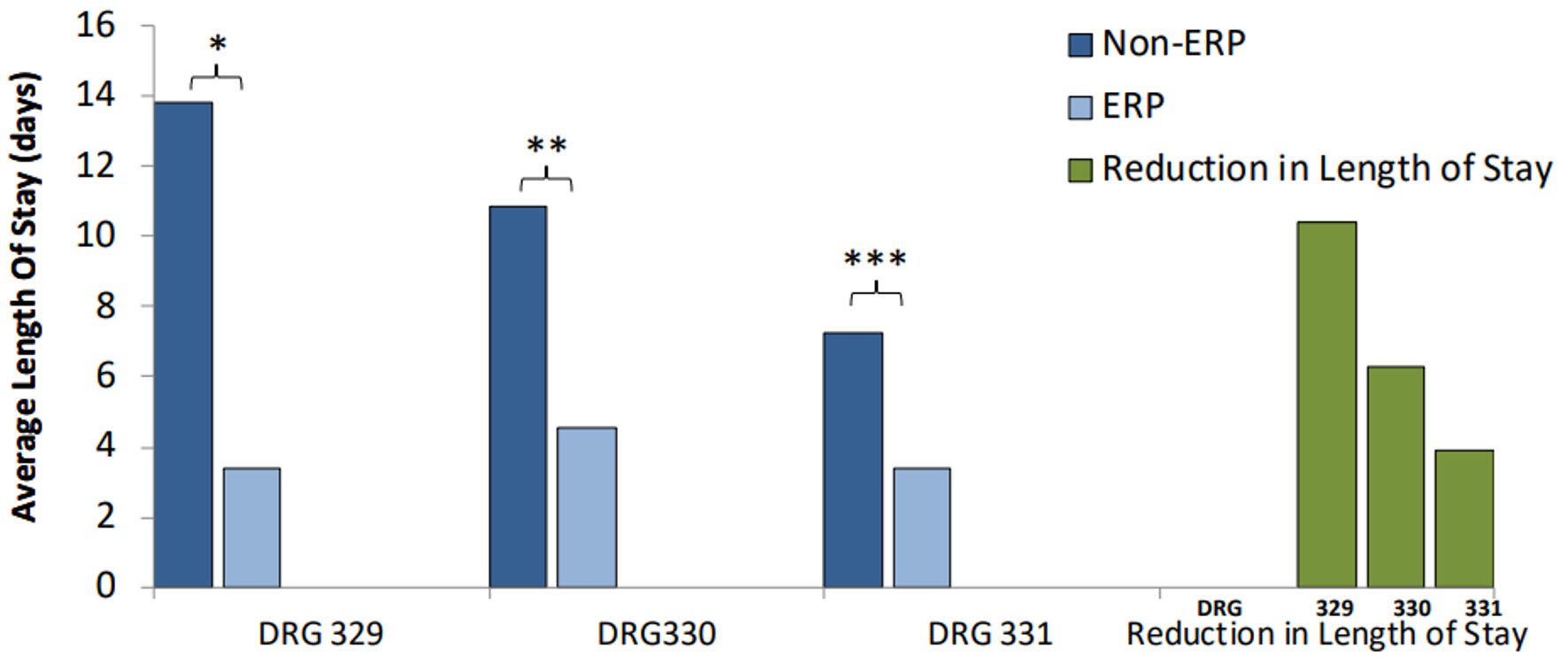
| Perioperative interventions | | |
| Counseling and education | Patient was provided counseling, booklet, and YouTube video on recovery program. Pre-habilitation initiated | At discretion of surgeon |
| Fluids and fasting | Fluid carbohydrate loading until 2 h before surgery. No solids foods after midnight | No fluids or solid food allowed after midnight before surgery |
| Bowel preparation | Minimal bowel preparation | At discretion of surgeon |
| Prophylaxis | DVT, infection, and hypothermia prophylaxis as per guidelines | DVT, infection, and hypothermia prophylaxis as per guidelines |
| Intraoperative interventions | | |
| Analgesia | Multimodal analgesia with no or short-acting premedication, minimal sedation and narcotics, routine use of nerve blocks | At discretion of surgeon |
| NGT | Sparing use of NGT, early removal postoperatively | Routine use at discretion of surgeon |
| Urinary catheter | Sparing use of Foley, early removal postoperatively | Routine use at discretion of surgeon |
| Drain | Sparing use of drain, early removal postoperatively | Routine use at discretion of surgeon |
| Surgical approach | Minimally invasive: laparoscopic/robotic | Minimally invasive: laparoscopic/robotic |
| Intravenous fluids | Avoid salt and water overload, minimal administration, dependent on operation | At discretion of surgeon |
| Hypothermia prevention | Active warm air blanket | Active warm air blanket |
| Postoperative interventions | | |
| Analgesia | Multimodal with minimal opioids | At discretion of surgeon |
| Mobilization | Early and frequent | At discretion of surgeon |
| Nutrition | Early oral nutrition, gum chewing | At discretion of surgeon |
| IV fluids | Minimal IV fluid hydration | At discretion of surgeon |