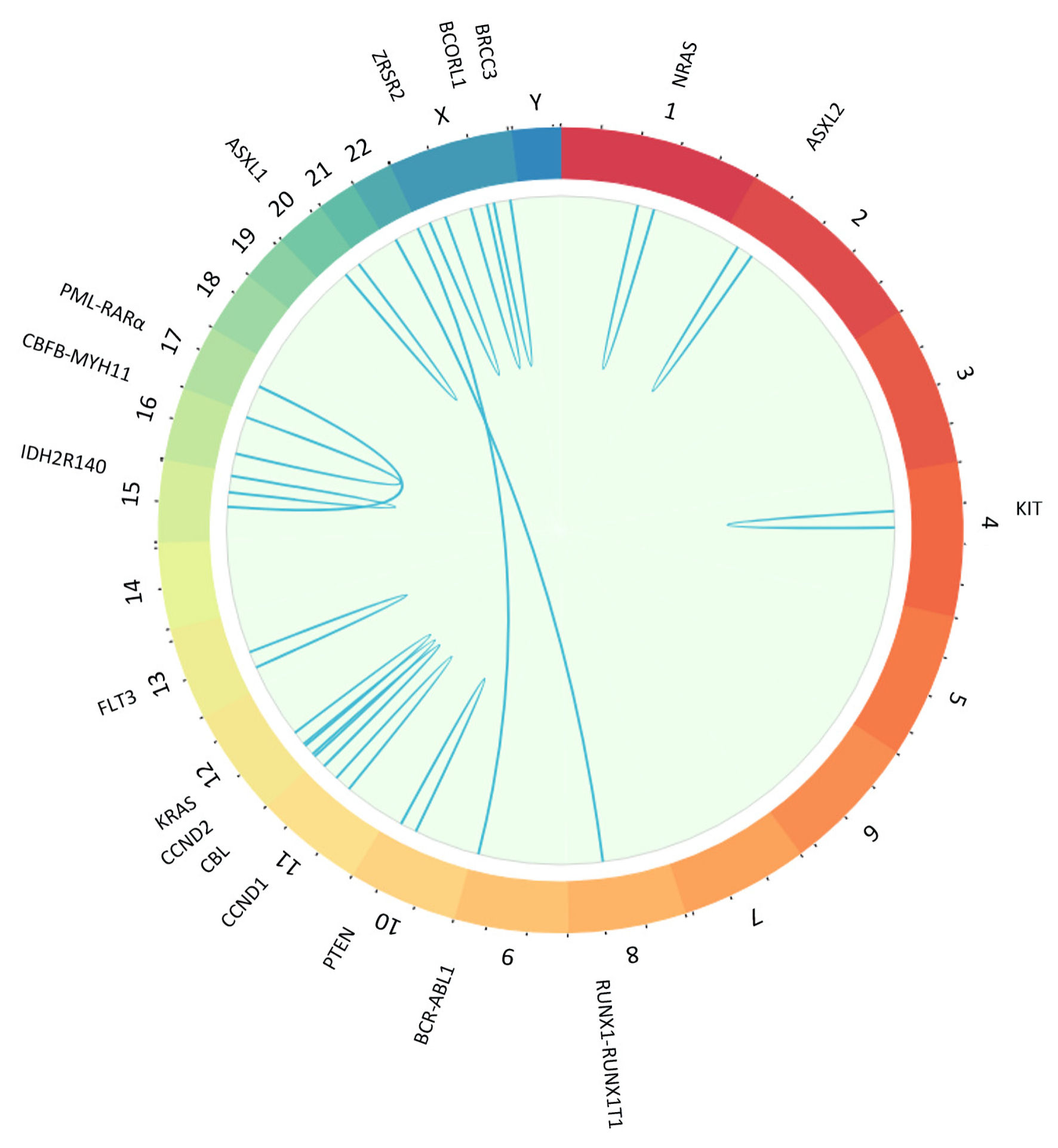
Figure 1. Plot created with BioCircos package in R showing with sky-blue lines secondary genetic mutations and gene fusions found in core binding factor acute myeloid leukemia (CBF-AML) cases in Mitelman Database. Chromosomes are individually colored and arranged clockwise from chromosome 1 to Y. We showed only mutations with a frequency greater than 1, and there were no rearrangements involving the Y chromosome. NRAS: neuroblastoma RAS viral gene mutation; ASXL2: ASXL transcriptional regulator 2 gene mutation; RUNX1-RUNX1T1: RUNX1-RUNX1 partner transcriptional co-repressor 1 genes fusion; BCR-ABL1: BCR-ABL1 fusion gene mutation; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homolog gene mutation; CCND1: cyclin D1 gene mutation; CCND2: cyclin D2 gene mutation; CBL: casitas B-lineage lymphoma gene mutation; KRAS: Kirsten rat sarcoma virus gene mutation; FLT3: FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 gene mutation; IDH2R140: isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 R140 gene mutation; CBFB-MYH11: core binding factor beta subunit-myosin heavy chain 11 genes fusion; PML-RARa: promyelocytic leukemia/retinoic acid receptor alpha gene mutation; ASXL1: ASXL transcriptional regulator 1 gene mutation; ZRSR2: zinc finger, RNA-binding motif and serine/arginine rich 2 gene mutation; BCORL1: BCORL1 gene mutation; BRCC3: BRCA1/BRCA2-containing complex 3 gene mutation.
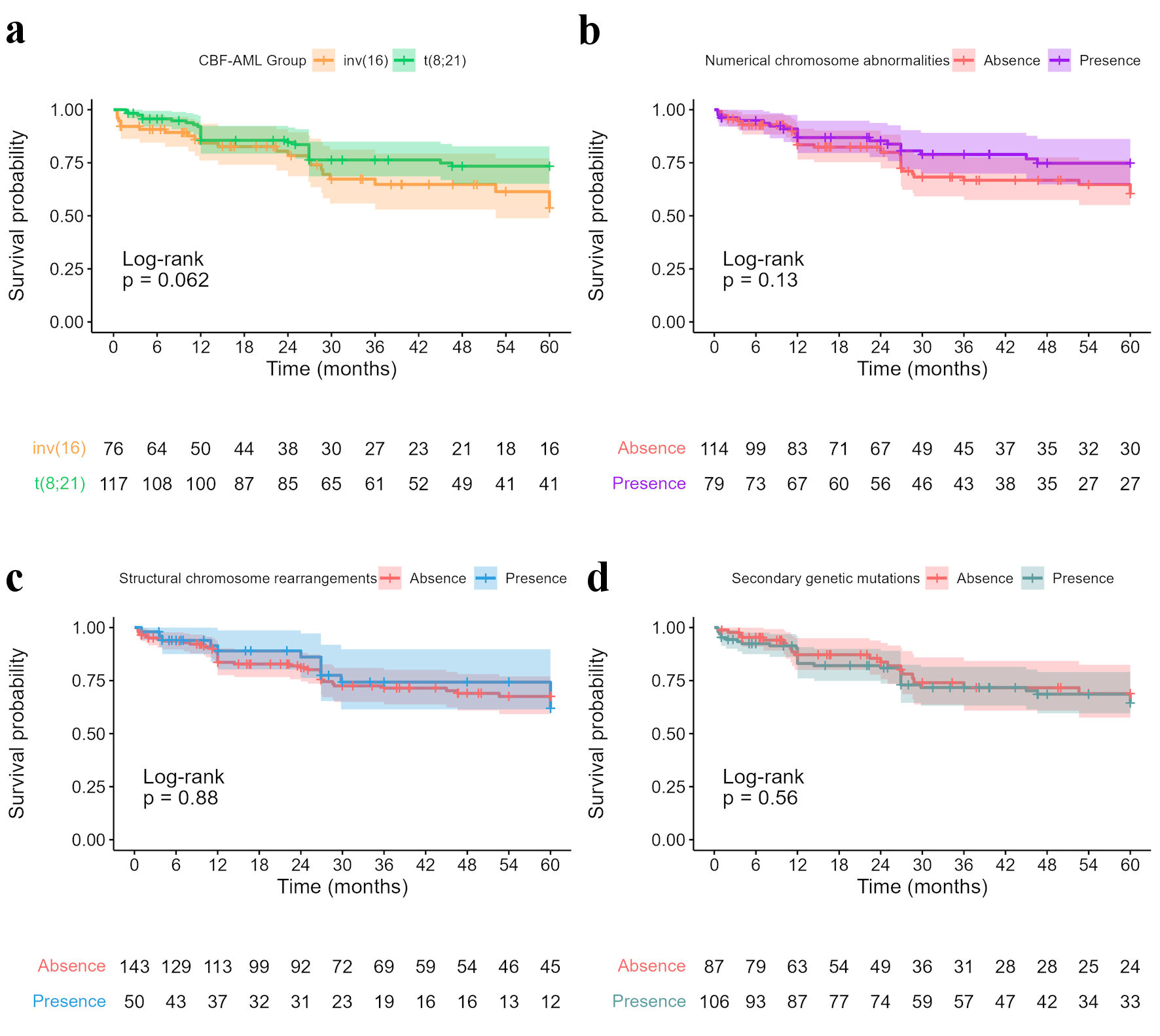
Figure 2. (a) Kaplan Meier curves for core binding factor acute myeloid leukemia (CBF-AML) groups showed no significant difference between groups. Five-year survival data of CBF-AML cases with secondary genetic findings: (b) Numerical chromosome abnormalities (5-year OS: 74.8%, 95% CI: 64.8 - 86.2, versus 60.4%, 95% CI: 50.1 - 72.9); (c) Structural chromosome rearrangements (5-year OS: 61.9%, 95% CI: 45.1 - 84.9, versus 67.5%, 95% CI: 59.2 - 77.0); (d) Secondary genetic mutations (5-year OS: 64.5%, 95% CI: 54.6 - 76.1, versus 68.9%, 95% CI: 57.5 - 82.4). CI: confidence interval; OS: overall survival.
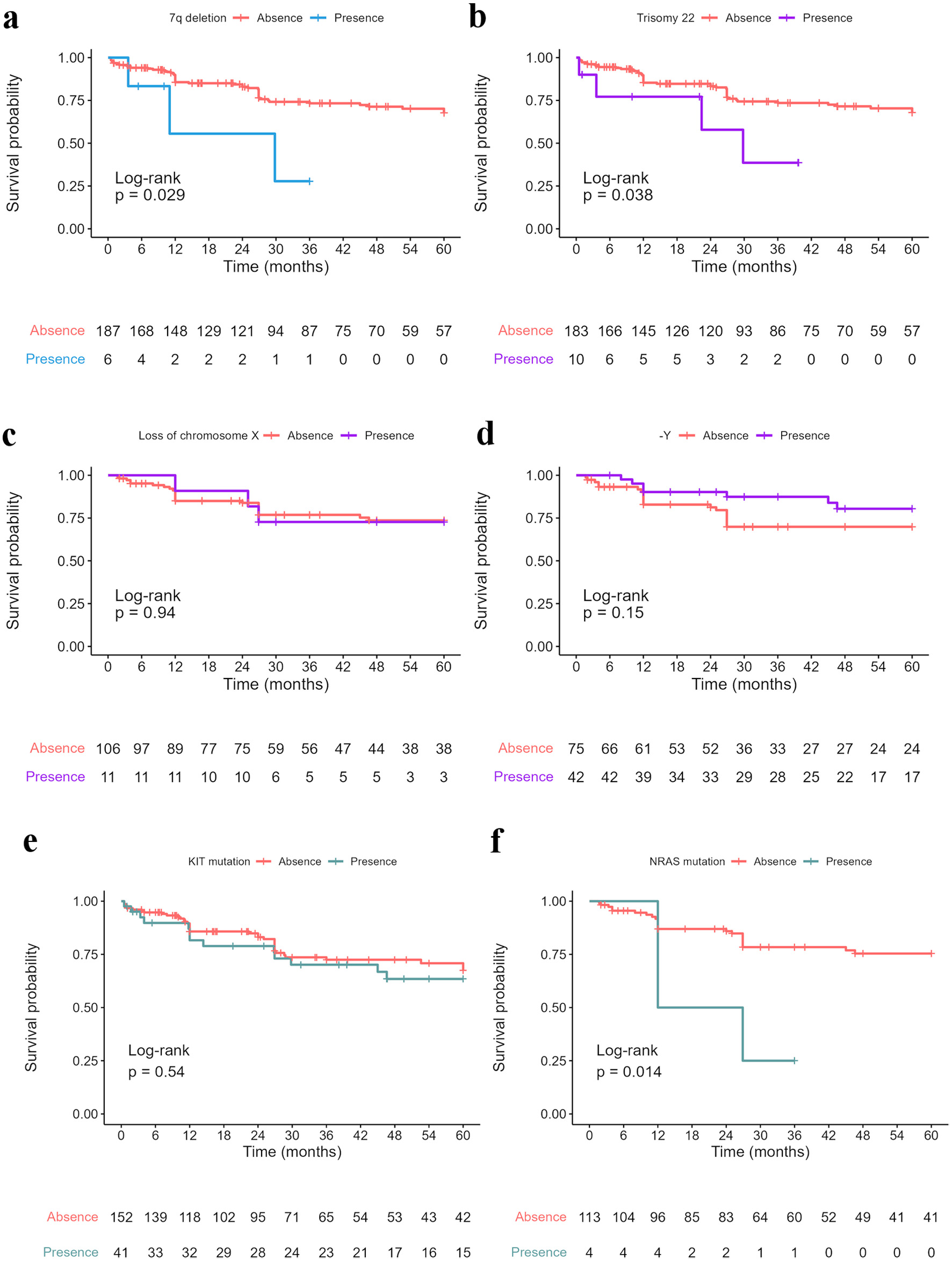
Figure 3. Five-year survival data of CBF-AML cases with specific secondary genetic aberration: (a) 7q deletion “del(7)” (5-year OS in total sample: 27.8%, 95% CI: 5.39 - 100, versus 67.7%, 95% CI: 60.1 - 76.2); (b) Trisomy 22 “+22” (5-year OS in total sample: 38.6%, 95% CI: 13.5 - 100, versus 67.9%, 95% CI: 60.2 - 76.5); (c) Loss of chromosome X “-X” (5-year OS in t(8;21) group: 72.7%, 95% CI: 50.6 - 100, versus 73.6%, 95% CI: 64.9 - 83.5); (d) Loss of chromosome Y “-Y” (5-year OS in t(8;21) group: 80.4%, 95% CI: 68.2 - 94.9, versus 69.9%, 95% CI: 59.6 - 82.0); (e) KIT mutation (5-year OS in total sample: 63.5%, 95% CI: 49.2 - 81.8, versus 67.4%, 95% CI: 58.7 - 77.4); (f) NRAS mutation (5-year OS in t(8;21) group: 25.0%, 95% CI: 4.58 - 100, versus 75.4%, 95% CI: 67.1 - 84.7). -Y: loss of chromosome Y; KIT: receptor tyrosine kinase gene KIT mutation; NRAS: neuroblastoma RAS viral gene mutation. CI: confidence interval; OS: overall survival.


