Figures
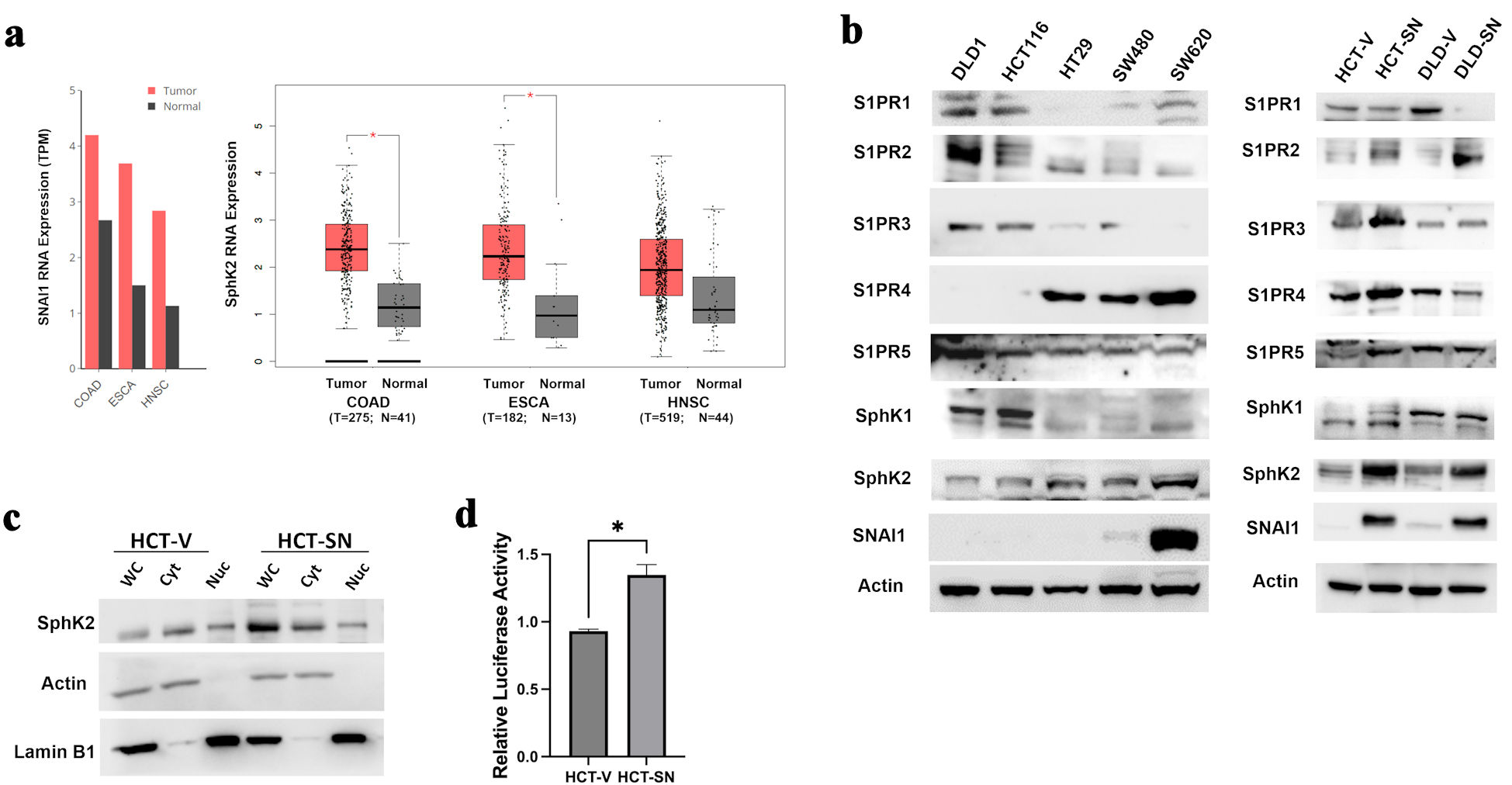
Figure 1. SNAI1 expression is associated with increased SPHK2 levels in CRC. (a) Comparisons of SNAI1 (left) and SPHK2 (right) RNA levels between tumoral and normal adjacent tissues in colorectal adenocarcinoma (COAD), esophageal adenocarcinoma (ESCA), and head and neck squamous cell cancer (HNSC) from TCGA datasets. Bars represent transcripts per million (TPM). Calculated means ± SEM are represented by bars and whiskers. *P < 0.05. (b) Western blot analysis for key S1P mediators in parental CRC cell lines (left panel) and ectopic-expressing SNAI1 cell lines compared with empty control vector cells (right panel). (c) Western blot analysis for SPHK2 in the cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of HCT-SN cell line, compared with empty control vector cells. (d) SPHK2 luciferase reporter activity of HCT-SN empty vector control cells transfected with SNAI1 siRNA, compared to control siRNA treated cells. CRC: colorectal cancer; SPHK2: sphingosine kinase 2; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; SEM: standard error of the mean; S1P: sphingosine-1-phosphate; S1PR: sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor.
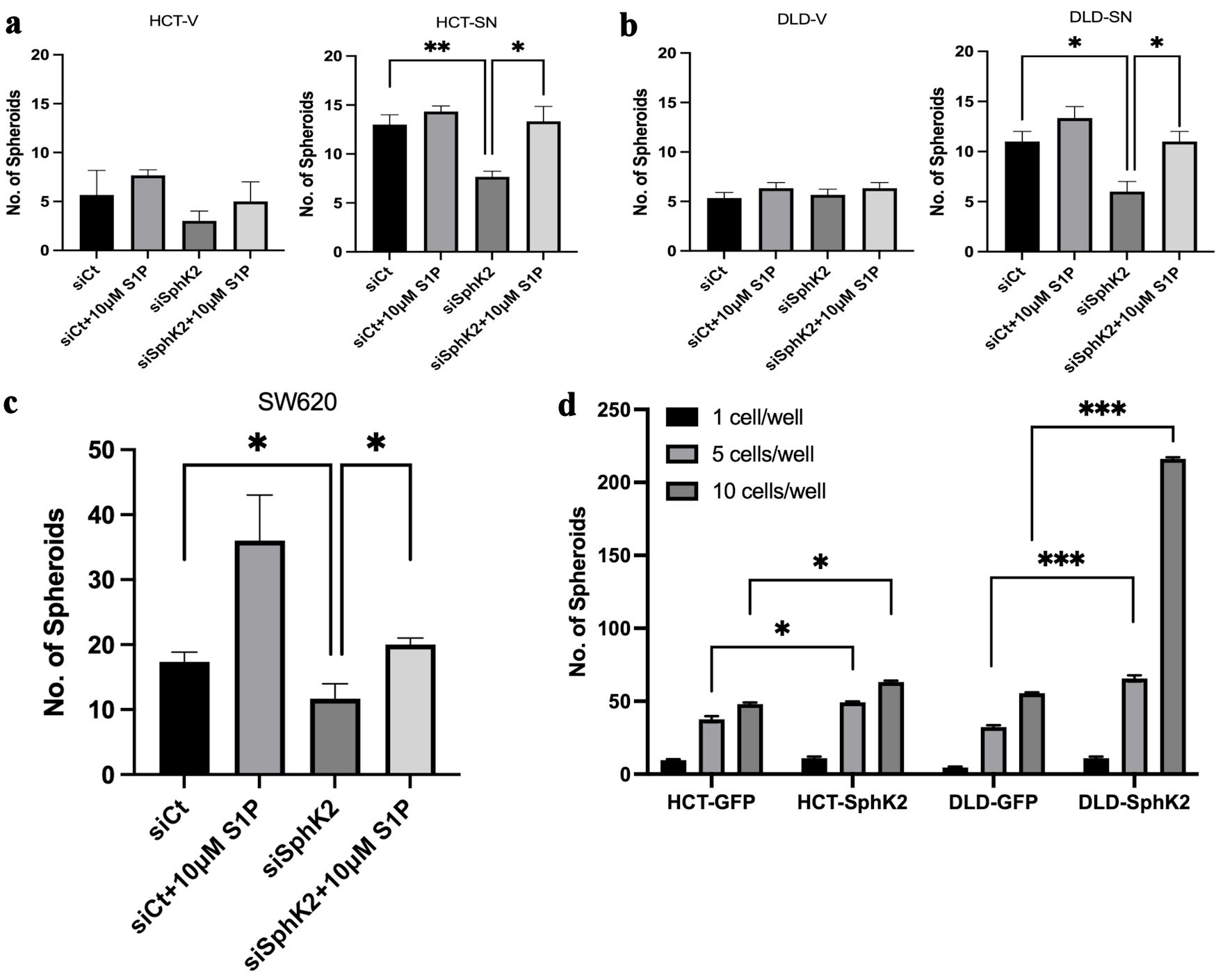
Figure 2. SPHK2 mediates stemness in ectopic SNAI1 expressing CRC cells. Limited dilution spheroid assay of (a) HCT-SN cells and (b) DLD-SN compared with empty vector control cells transfected with siSPHK2 or control for 10 days. (c) Limited dilution spheroid assay of SW620 cells transfected with siSPHK2 or control for 10 days. (d) Limited dilution spheroid assay comparing HCT-SPHK2 and DLD-SPHK2 cells with GFP vector (GFP) control cells. Limited dilution was performed with one cell or five cells or 10 cells per well. Data are shown as mean ± SD (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005). CRC: colorectal cancer; SPHK2: sphingosine kinase 2; S1P: sphingosine-1-phosphate; SD: standard deviation.
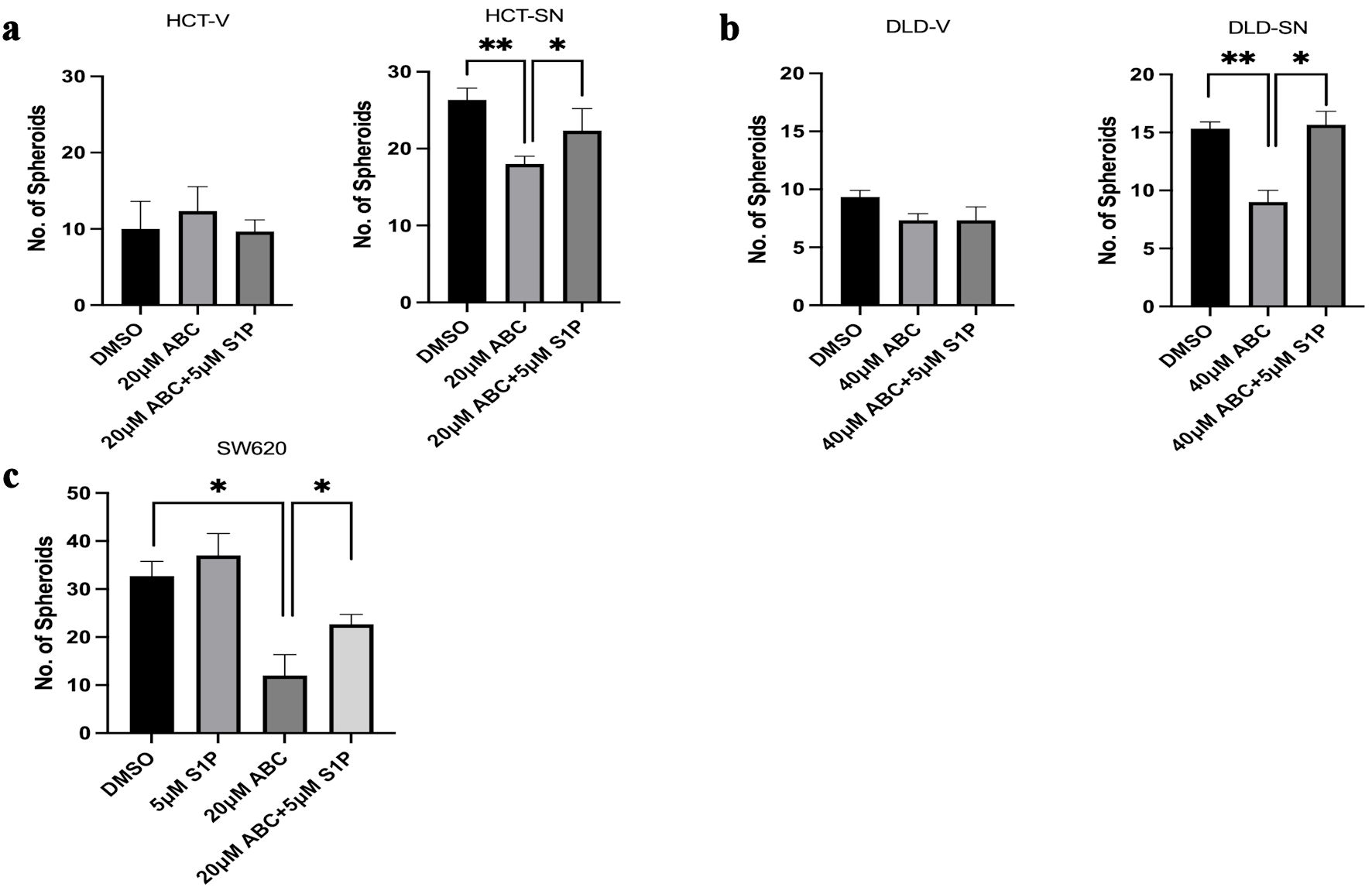
Figure 3. SNAI1-mediated stemness can be ablated by ABC294640. Limited dilution spheroid assay of (a) HCT-SN cells, and (b) DLD-SN cells, compared with empty vector control cells after ABC294640 treatment compared with vehicle control (DMSO). (c) Limited dilution spheroid assay of SW620 cells after ABC294640 treatment compared with vehicle control (DMSO). Rescue experiments were performed with S1P. Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 12 (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). S1P: sphingosine-1-phosphate; SD: standard deviation.
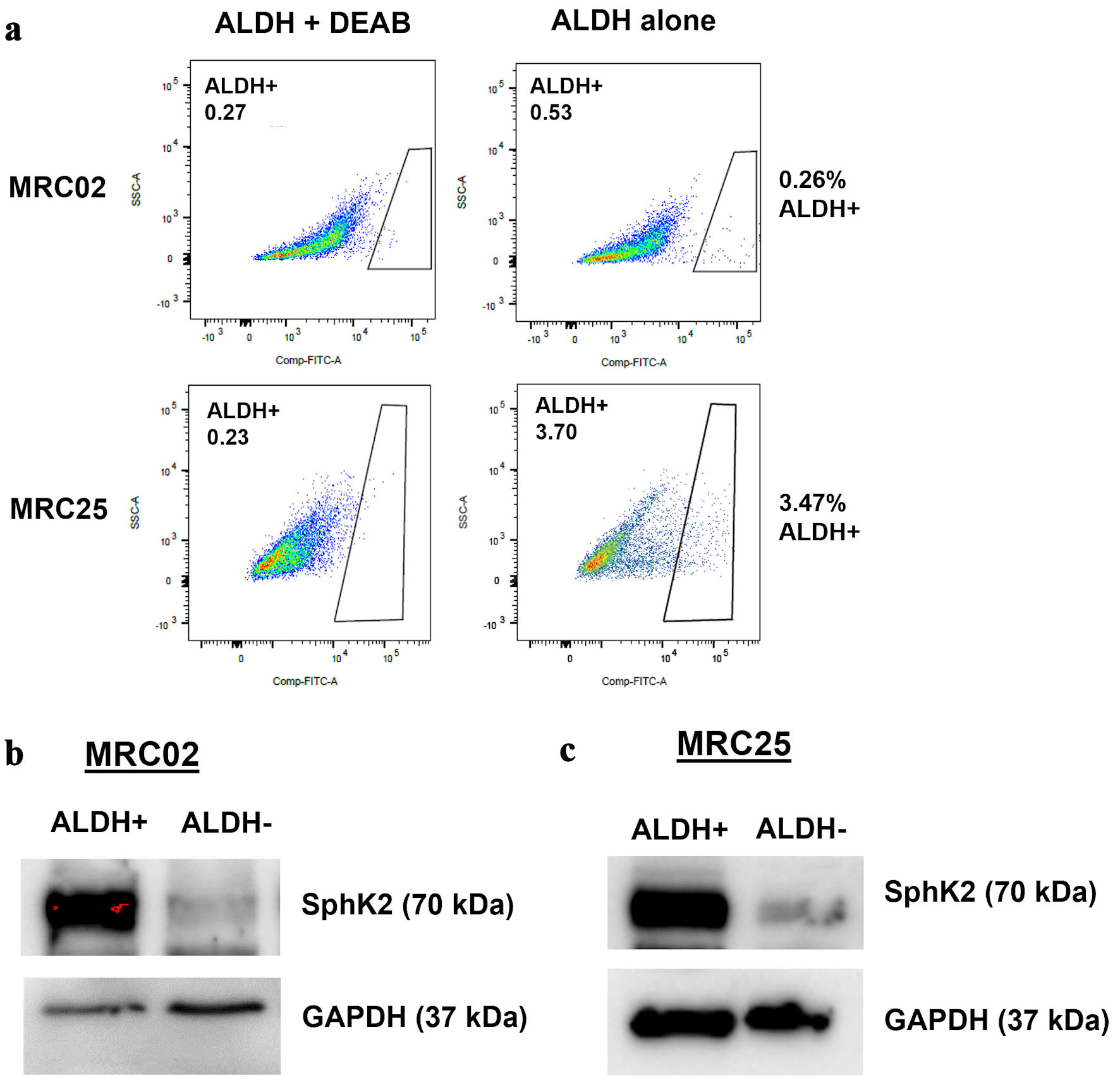
Figure 4. SPHK2 is overexpressed in colorectal cancer stem cells. (a) Representative flow cytometry analysis of aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activity with and without (N, N-diethylamino)benzaldehyde (DEAB), an inhibitor of ALDH in two patient-derived xenograft tumors: MRC02 and MRC25. (b, c) Western blot analysis for expression of SPHK2 in MRC02 and MRC25. SPHK2: sphingosine kinase 2; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
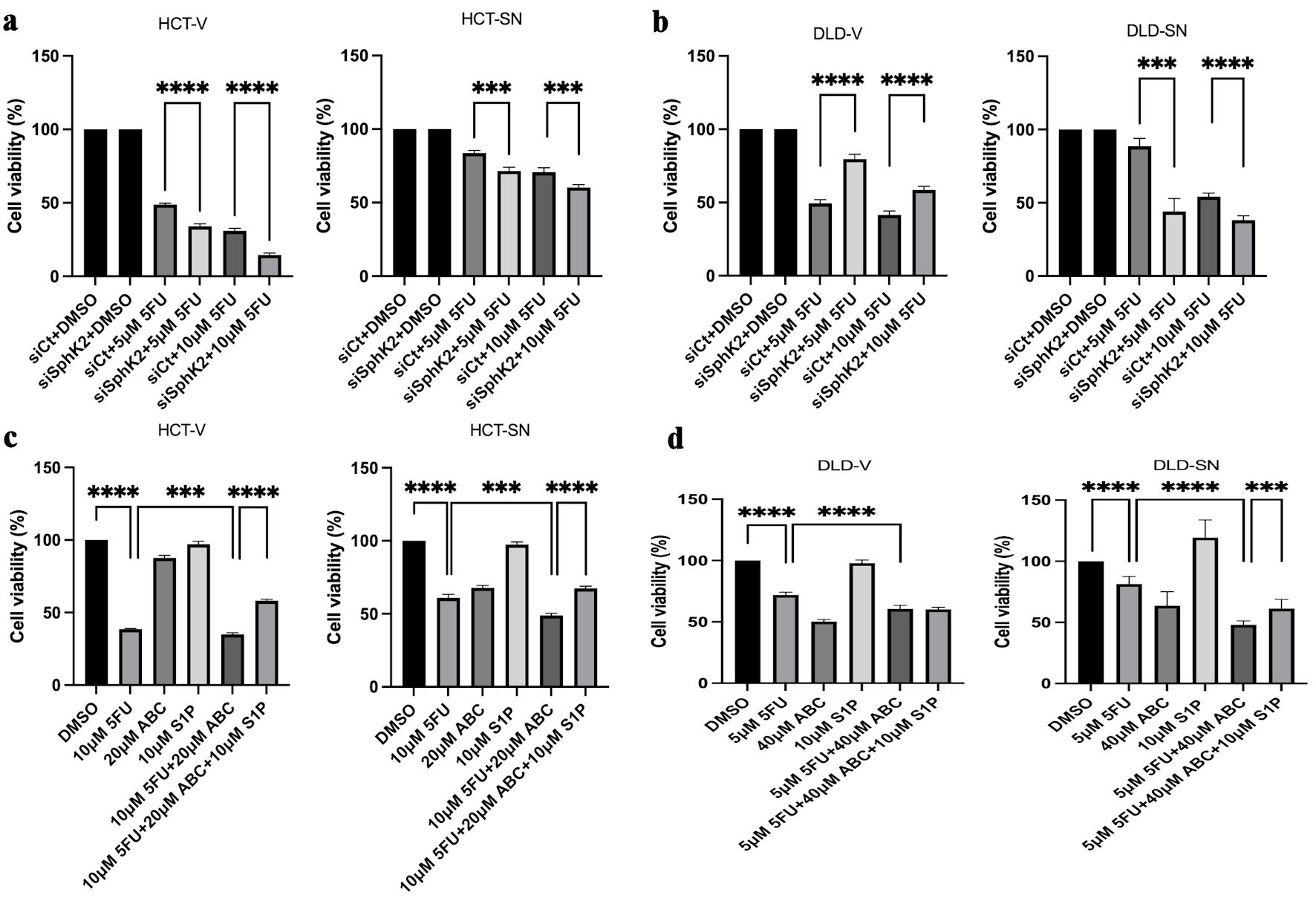
Figure 5. SPHK2 inhibition increases 5FU sensitivity in ectopic SNAI1 expressing CRC cells. Cell viability was assessed 96 h after 5FU treatment compared with vehicle control (DMSO) in (a) HCT-SN cells and (b) DLD-SN cells compared with empty vector control cells transfected with SPHK2 siRNA or control siRNA. Similarly, cell viability was assessed 96 h after treatment with 5FU, ABC294640, or the combination in (c) HCT-SN cells, or (d) DLD-SN cells and compared with empty vector control cells (left and right panel). Rescue experiments were performed with S1P. Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 5 (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005, ****P < 0.001). CRC: colorectal cancer; SPHK2: sphingosine kinase 2; 5FU: 5-fluorouracil; SD: standard deviation.
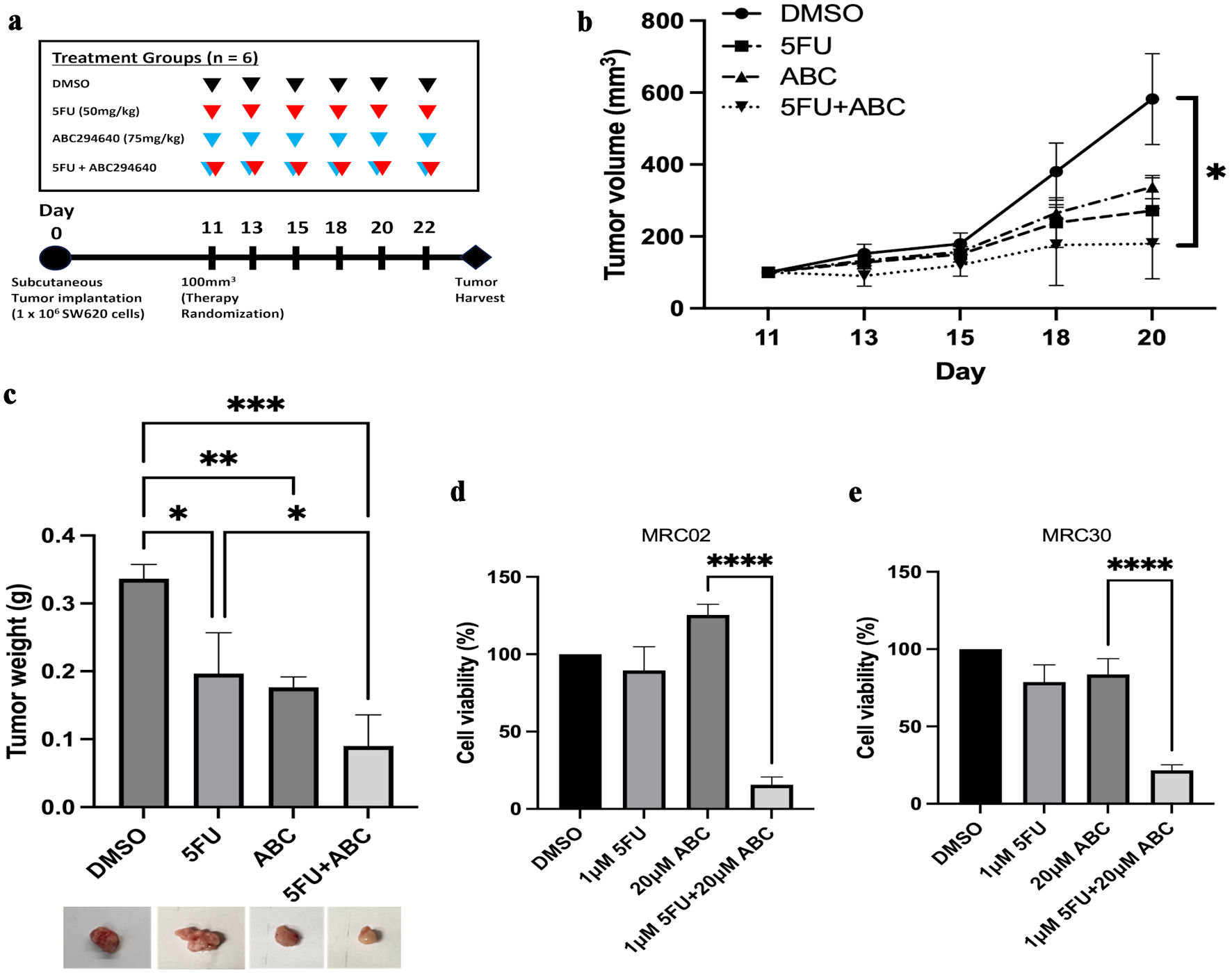
Figure 6. ABC294640 increases 5FU sensitivity in SW620 in vivo xenografts and CRC PDTOs. Following treatment for 11 days, subcutaneous tumors were harvested and analyzed. (a) In vivo experimental schema. After subcutaneous injection of SW620 cells, mice were randomized to four treatment groups of six mice each, starting 11 days postoperatively. 5FU (50 mg/kg) (red arrows) and 75 mg/kg of ABC294640 (blue arrows) were intraperitoneally injected three times per week. Tumors were harvested 20 - 22 days after tumor implantation. (b) Average measured tumor volume of subcutaneous SW620 xenografts throughout treatment. (c) Average tumor weight of harvested SW620 xenografts. The error bars represent mean ± SD; n = 3 (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005). (d, e) Cell viability was assessed 96 h after 5FU or ABC294640 treatment compared with vehicle control (DMSO) in two PDTO models: MRC02 (c), and MRC30 (d). Data are shown as mean ± SD; n = 5 (****P < 0.001). CRC: colorectal cancer; 5FU: 5-fluorouracil; SD: standard deviation; PDTOs: patient-derived tumor organoids.





