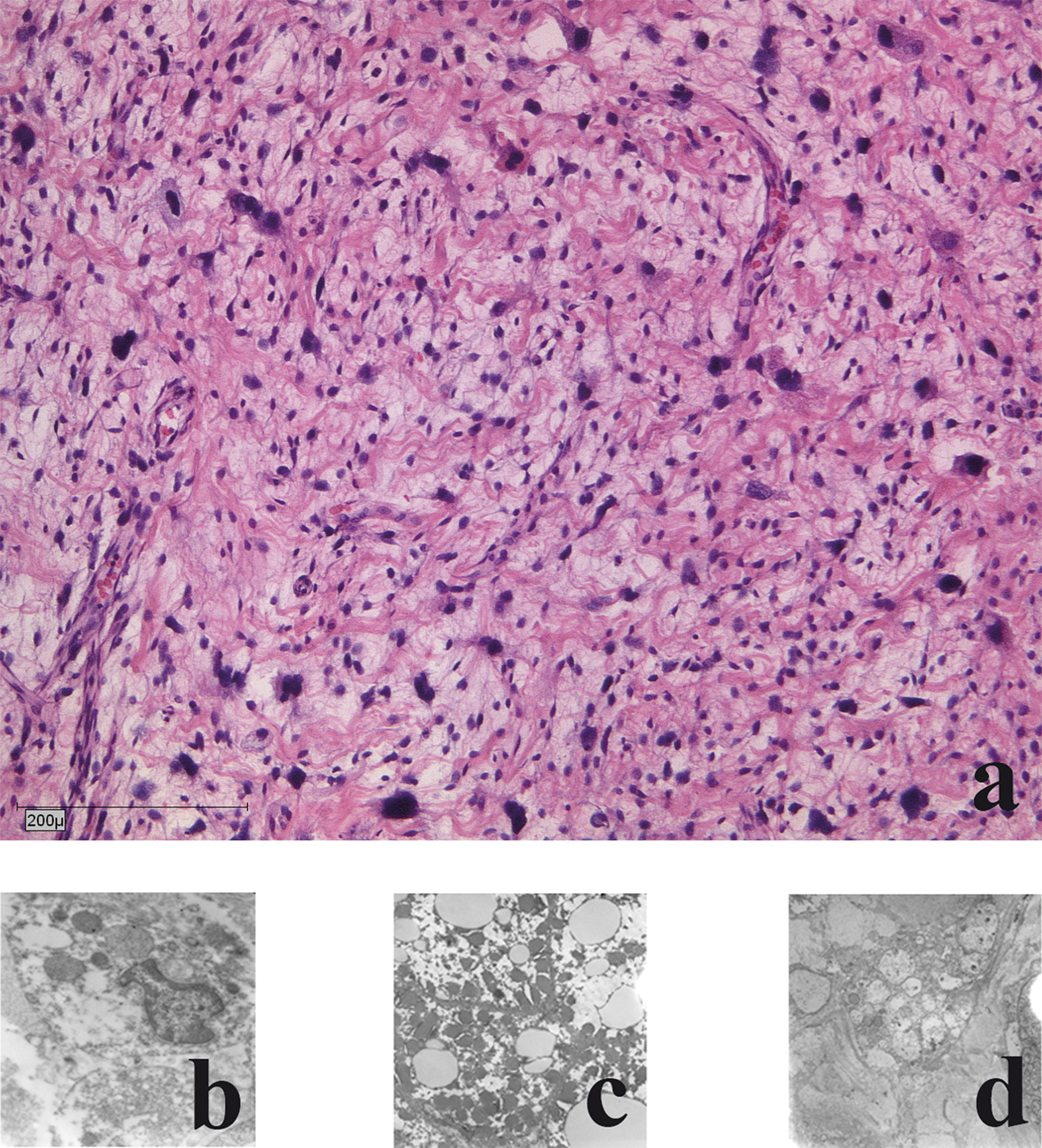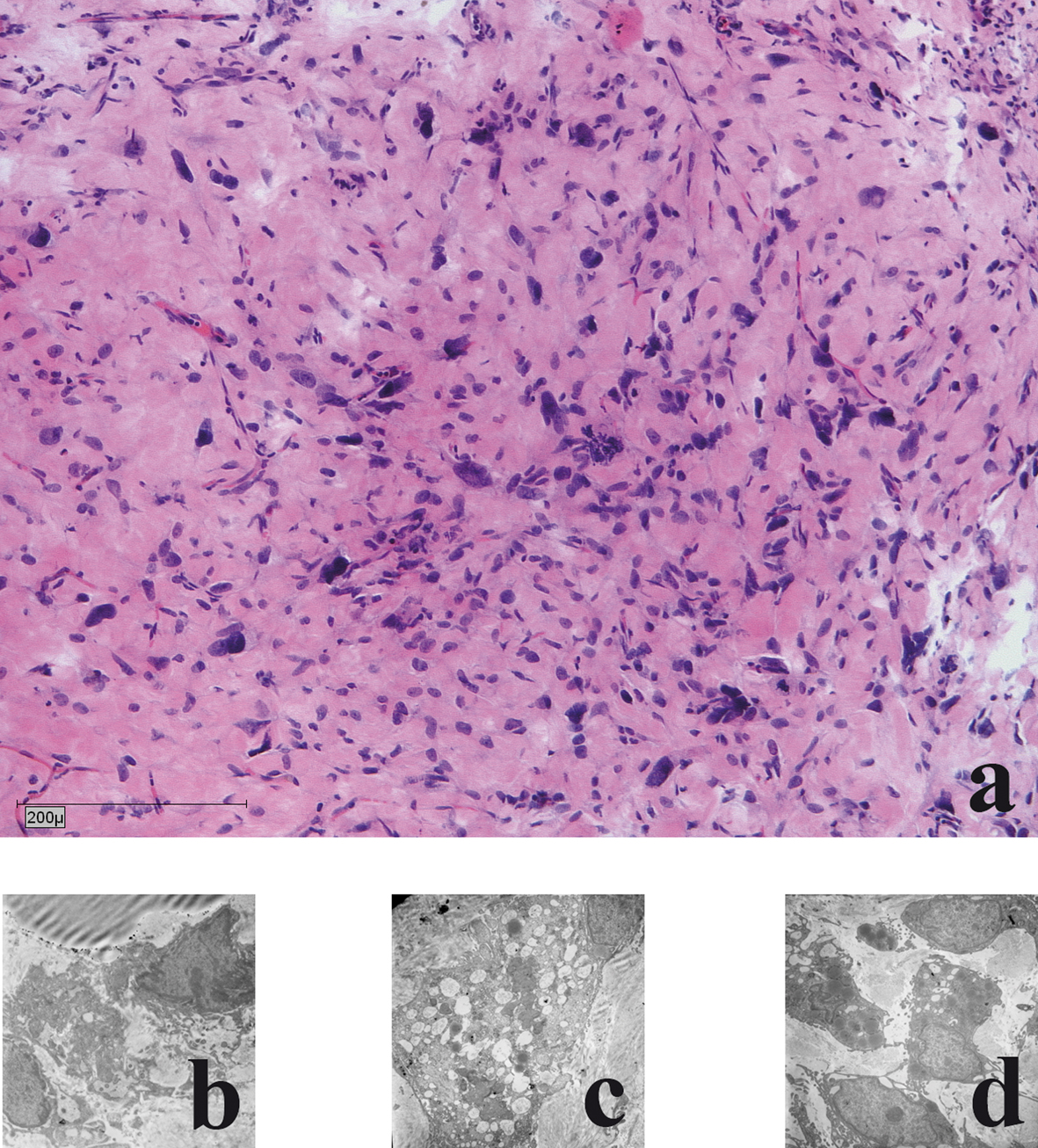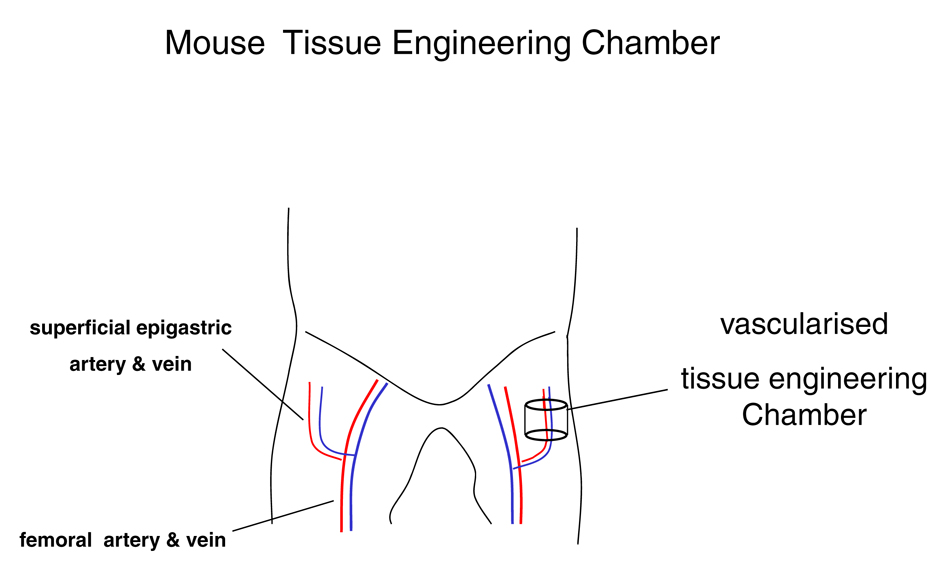
Figure 1. Mouse vascularised tissue engineering groin chamber model for growing primary human liposarcoma.
| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.wjon.org |
Original Article
Volume 3, Number 2, April 2012, pages 47-53
The Vascularised Groin Chamber: A Novel Model for Growing Primary Human Liposarcoma in Nude Mice
Figures