Figures
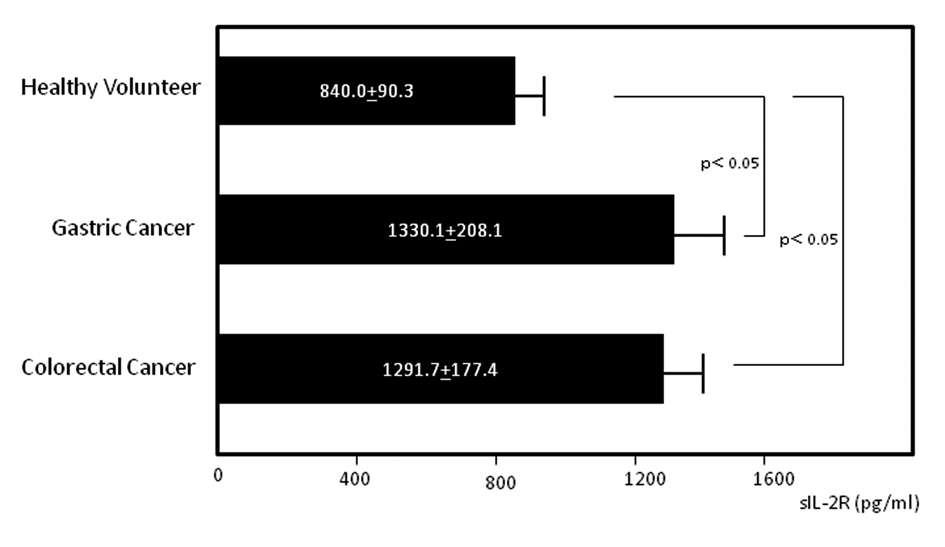
Figure 1. Serum levels of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R). Serum sIL-2R concentrations in gastric and colorectal cancer patients and healthy volunteers.
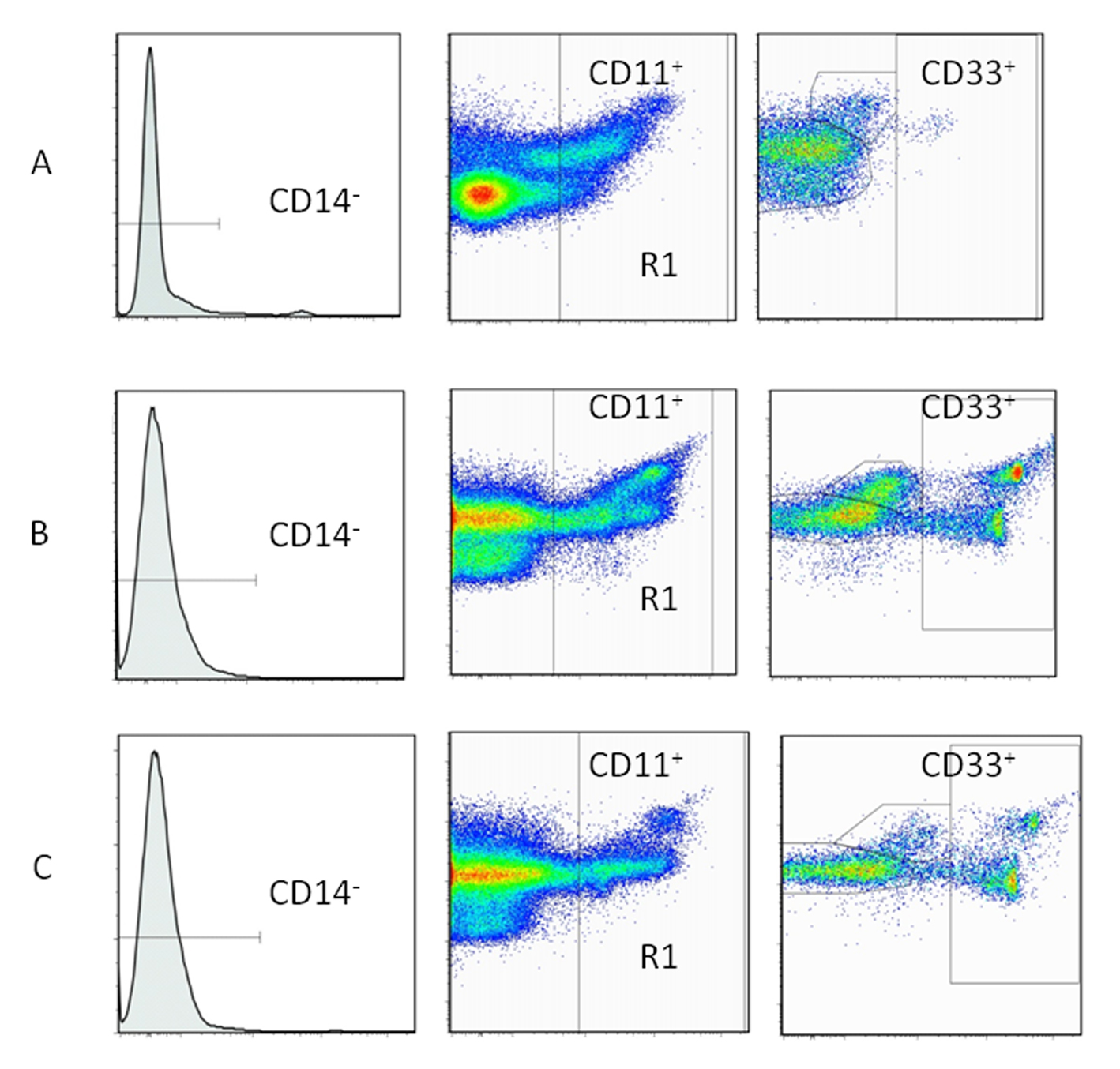
Figure 2. Immunophenotyping of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) by flow cytometry. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) used for the flow cytometric analysis of MDSCs (CD11b+, CD14-, CD33+). A: healthy volunteers. B: gastric cancer patients. C: colorectal cancer patients.
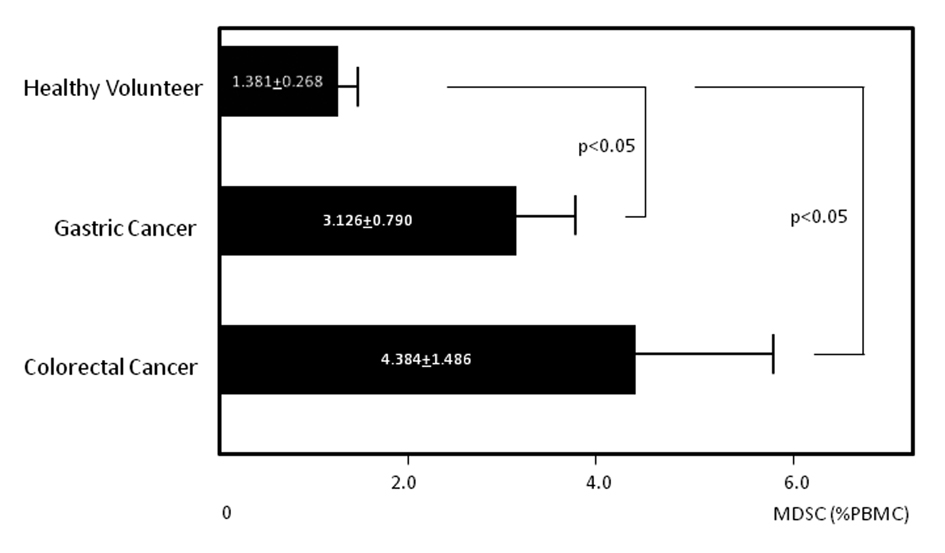
Figure 3. Circulating levels of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Circulating levels of MDSCs in gastric and colorectal cancer patients and healthy volunteers.
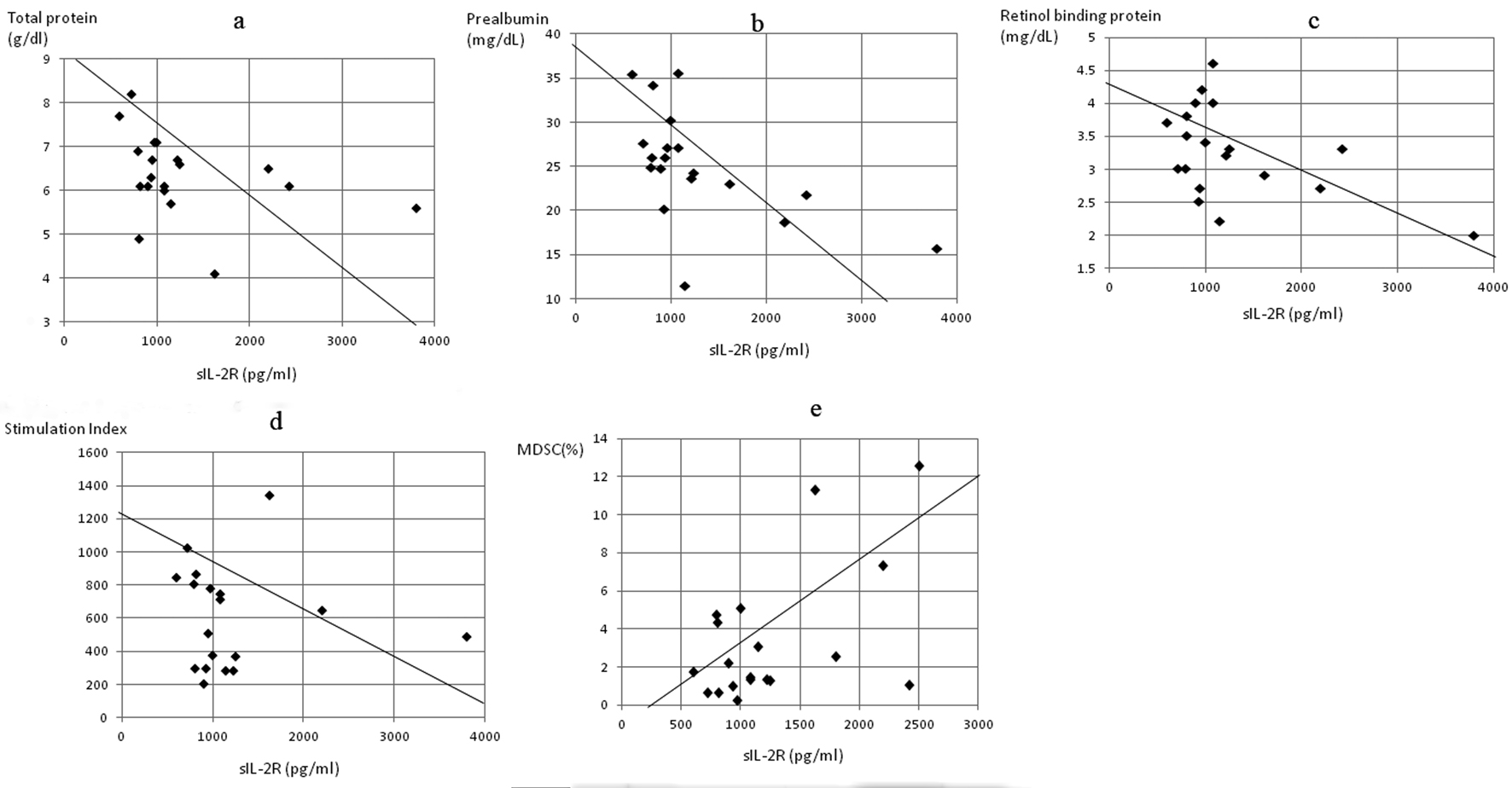
Figure 4. Correlation of serum concentrations of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) to markers of nutrition, cell-mediated immunity and MDSC concentration in gastric cancer patients. The sIL-2R level was significantly inversely correlated to (a) total protein (P < 0.05, r = -0.413), (b) prealbumin (P < 0.0005, r = -0.784), (c) retinol binding protein (P < 0.05, r = -0.495), and (d) stimulation index (P < 0.05, r = -0.512), and positively correlated to (e) MDSC levels (P < 0.05, r = 0.482).
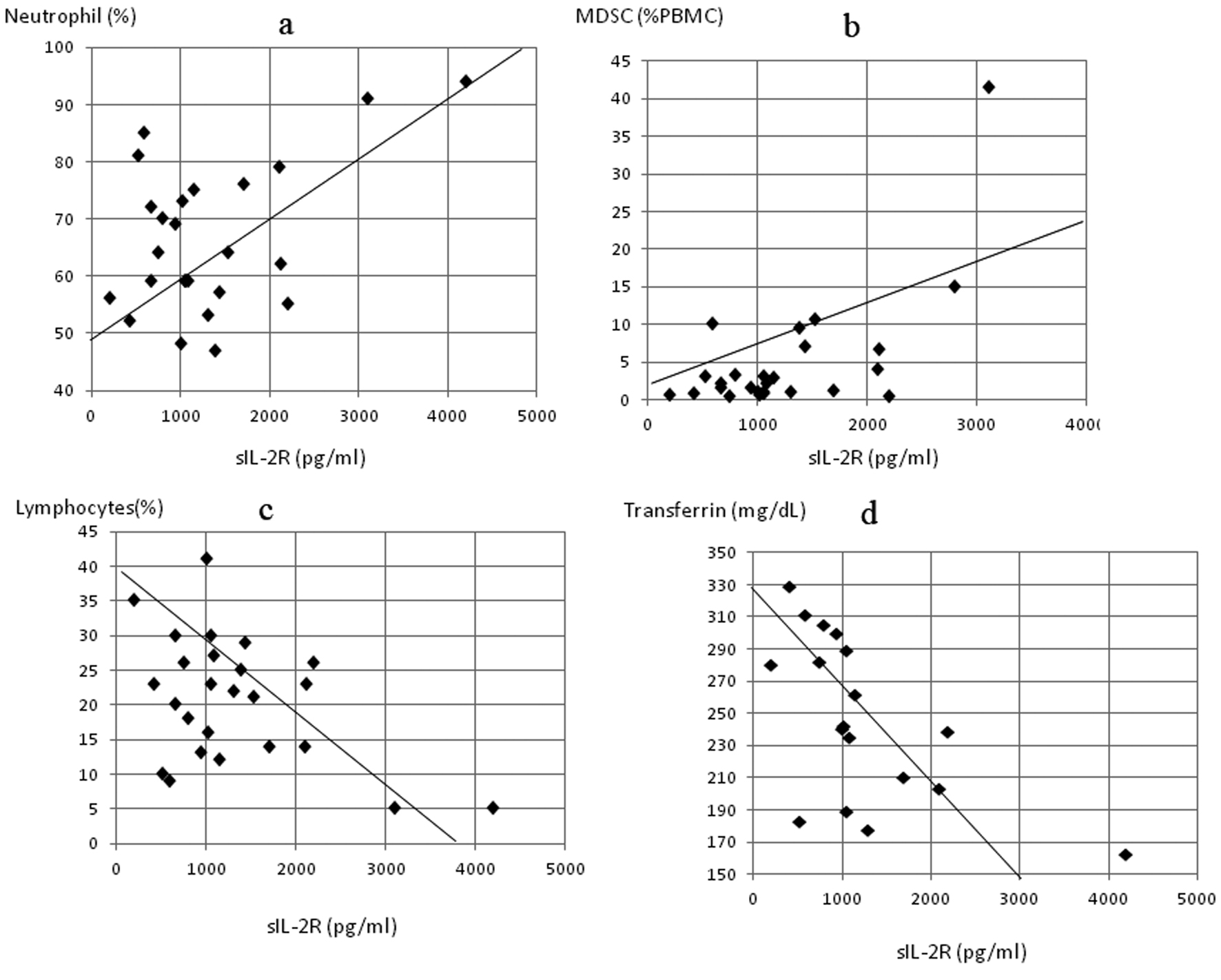
Figure 5. Correlation of serum concentrations of soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL-2R) to markers of inflammation, nutrition and MDSC concentration in colorectal cancer patients, sIL-2R significantly correlated to (a) neutrophil count (P < 0.01, r = 0.501) and (b) MDSC levels (P < 0.05, r = 0.453) and inversely correlated to (c) lymphocyte count (P < 0.05, r = -0.472) and (d) serum transferrin (P < 0.0005, r = -0.614).





