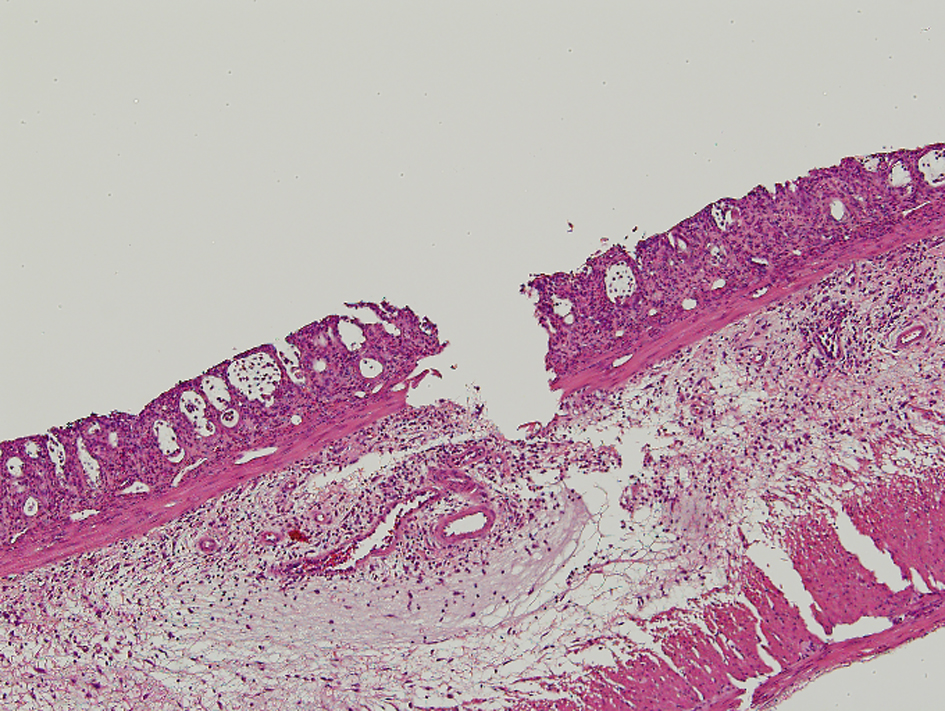
Figure 1. In the pathologic findings, crypt architectural distortion with inflammatory cells, loss of the columnar shape, and the submucosal edema were observed. The loss of epithelium reached submucosa through muscularis mucosa for Grade 4 in the morphological damage. The degree of inflammation was severe and corresponded to Grade 4.