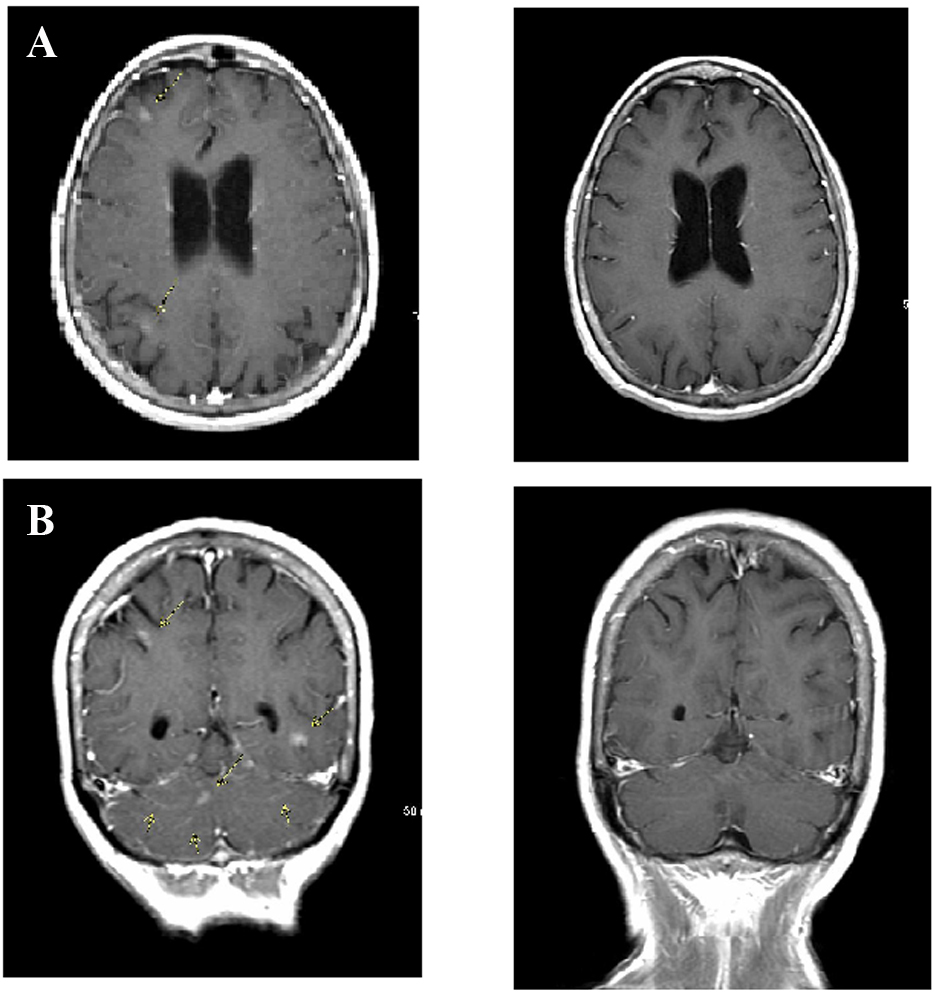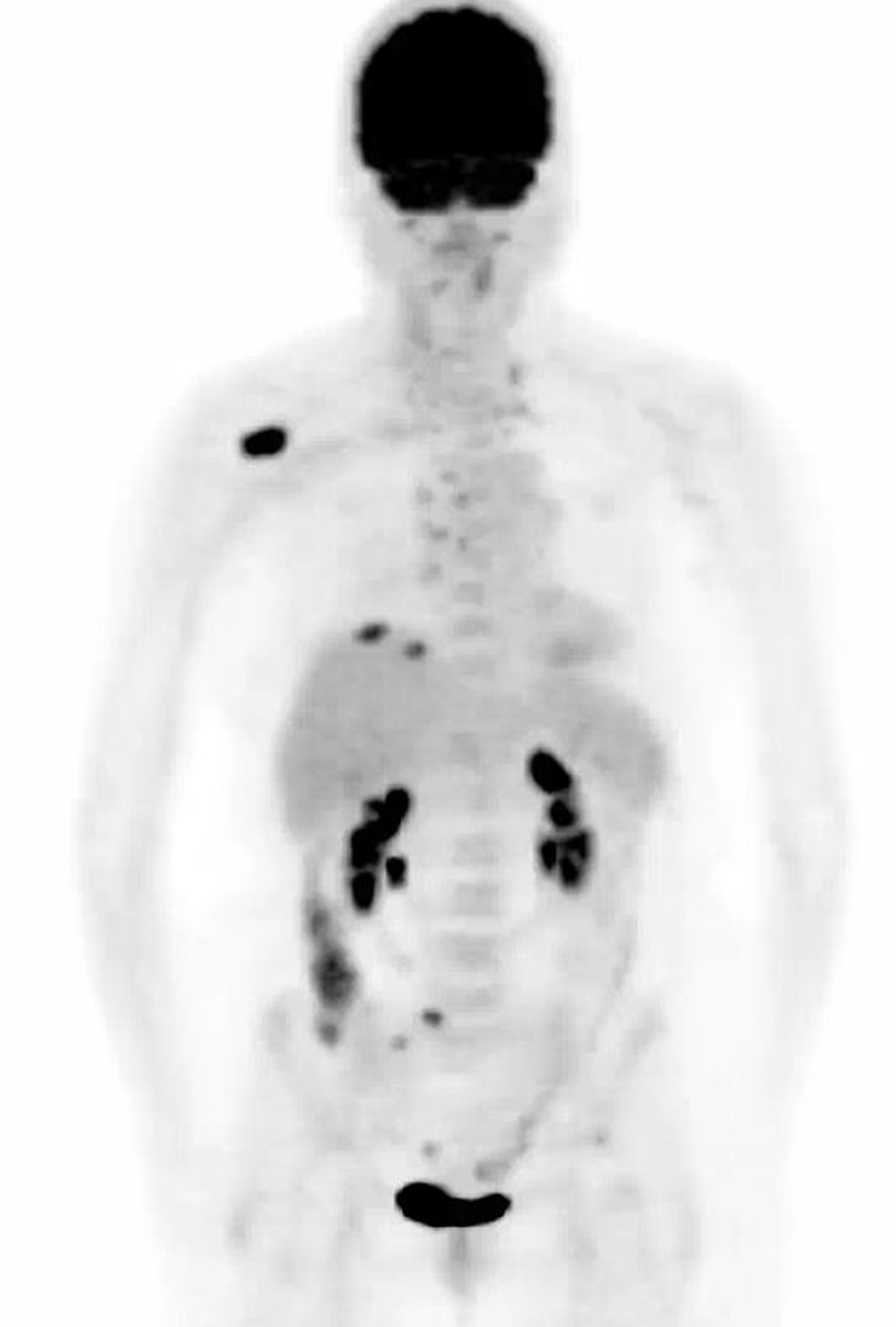
Figure 1. Computed tomography-positron emission tomography performed prior to treatment. Maximum intensity projection image shows mass within right lung base. Adenopathy with abnormal uptake is present throughout the mediastinum and neck. Largest bone metastasis involves right scapula.