| World Journal of Oncology, ISSN 1920-4531 print, 1920-454X online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, World J Oncol and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.wjon.org |
Original Article
Volume 12, Number 5, October 2021, pages 173-177
Impact of Testicular Germ Cell Tumor Laterality on Recurrence-Free Survival in the Mexican Population
David Davila Duponta, Daniel Motola Kubaa, Thalia de los Milagros Alcantara Velardeb, Erika Adriana Martinez Castanedaa, Rita Dorantes Herediaa, Jose Manuel Ruiz Moralesa, c
aHospital Medica Sur, Mexico City, Mexico
bHospital ABC Observatorio, Mexico City, Mexico
cCorresponding Author: Jose Manuel Ruiz Morales, Hospital Medica Sur, Mexico City, Mexico
Manuscript submitted August 12, 2021, accepted September 9, 2021, published online September 15, 2021
Short title: Impact of TGCT Laterality on RFS
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon1404
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Background: To date, the prognostic value of laterality for testicular germ cell tumors remains unknown. Herein, we describe this prognostic factor in the Mexican population.
Methods: A retrospective single-center study that included 37 patients with primary testicular germ cell tumors was conducted. Primary outcome was recurrence-free survival (RFS) at 2 years. Secondary outcomes were RFS by histology, progression-free survival by laterality, and 2-year overall survival.
Results: Thirty-seven patients were included, of which five showed relapses. By laterality, the 2-year RFS rate was 100% for left tumors and 77.3% for right tumors, with a trend toward statistical significance (P = 0.058). By histology, the RFS rate was higher for seminomas than non-seminomas (89% vs. 83%, respectively) without this difference being statistically significant. Progression-free survival was higher for right tumors than left tumors (91% vs. 80%, respectively) but without reaching statistical significance. The overall survival rate for the entire cohort was 94.5%.
Conclusions: Our study shows that patients with primary germ cell tumors of the right testicle have a higher risk of recurrence than those with primary germ cell tumors of the left testicle, with a trend toward statistical significance.
Keywords: Laterality; Recurrence; Right; Left; Seminoma; Non-seminoma
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Testicular germ cell tumors are the most common solid malignant neoplasms in young adults, and their prognosis is one of the most favorable in terms of malignant diseases. Currently, the primary treatment and options for adjuvant and rescue treatment in case of relapse are well established [1].
Certain risk factors for testicular germ cell tumors, such as lymphovascular invasion, size, and rete testis invasion, have been identified. These risk factors in stage I disease may cause a greater risk of early recurrence, which is defined as the evidence of disease before 2 years post diagnosis. However, the prognostic value of laterality of the primary tumor site is unknown [1].
Venous drainage could play an important role in early recurrences because the anatomy of each testicle is different. The right testicular venous drainage occurs in the vena cava while the left testicular venous drainage occurs in the left renal vein, with a predictable pattern of lymphatic dissemination. For this reason, this study was conducted to verify whether tumors of the right testicle present a higher risk of early recurrence than those of the left testicle [2].
The pattern of lymphatic dissemination in the retroperitoneum for this type of neoplasia is predictable. Typically, tumors originating from the right testicle mainly involve the interaortocaval nodes, while those originating from the left testicle involve the para-aortic nodes [3].
Limited information is available regarding the prognostic value of laterality for testicular germ cell tumors. An Australian study published in 1991, with more than 1,000 patients from a retrospective cohort, found that germ cell tumors are slightly predominant in the right testicle; however, it did not describe the prognostic value of this finding [4].
Thus, this retrospective single-center study was performed to determine the role of laterality in recurrence-free survival (RFS) at 2 years.
| Materials and Methods | ▴Top |
Study design and participants
This is an observational, descriptive, nonrandomized, single-center study. Eligible participants were aged ≥ 18 years, with a primary testicular germ cell tumor, stage I - III according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) eighth edition classification and a follow-up of ≥ 2 years. Participants were excluded if they had bilateral testicular tumors or extratesticular primary germ cell tumors.
The study protocol was approved by a research ethics committee and was performed in accordance with Good clinical practice standards and the Declaration of Helsinki. The study protocol and subsequent amendments were approved by our Institutional Ethics Committee.
Outcomes
The primary outcome was the RFS at 2 years, which was defined as the time at which a recurrence was detected in patients who underwent orchiectomy ± adjuvant chemotherapy and who were disease free. The secondary outcomes were RFS by histology, progression-free survival (PFS) by laterality (defined as the presence of new lesions, an increase of 30% or more in size in the target lesions or death) and 2-year overall survival (OS; defined as the proportion of patients who remained alive, regardless of disease progression).
Statistical analysis
The target sample size was approximately 39 participants to ensure an adequate number of patients for analysis. We estimated a 20% reduction in the primary outcome with this sample size, with a P < 0.05 for statistical significance. Statistical analysis by intention to treat was performed using IBM SPSS software. Survival curves were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method.
| Results | ▴Top |
From 2017 to 2019, 45 patients with a diagnosis of primary testicular germ cell tumor were analyzed in our hospital, regardless of histology, stage, and/or prognostic group. Eight patients were excluded from this study due to lack of information. For the 37 patients included, the median age was 33 years (range: 19 - 53 years), the proportion of seminoma and non-seminoma cases was similar (51% vs. 49%), and left testicular tumors represented 41% of cases while right testicular tumors accounted for 59% of cases. Other characteristics of the patients are summarized in Table 1.
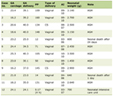 Click to view | Table 1. The Characteristics of the Patients |
The primary outcome (RFS at 2 years) showed a trend toward statistical significance. We found that five patients had recurrence and all of them were related to tumors of the right testicle with 2-year RFS rates of 100% and 77.3% in the left-side and the right-side testicular germ cell tumors, respectively (P = 0.058, Fig. 1). The 2-year RFS rate for the entire cohort was 86.5%. Four recurrences in the retroperitoneum and one distant recurrence were observed: three cases in initial stage IB, one case in initial stage IA, and one case in initial stage IIB that had shown a complete response with chemotherapy. Three recurrences occurred during active surveillance and two occurred after adjuvant chemotherapy.
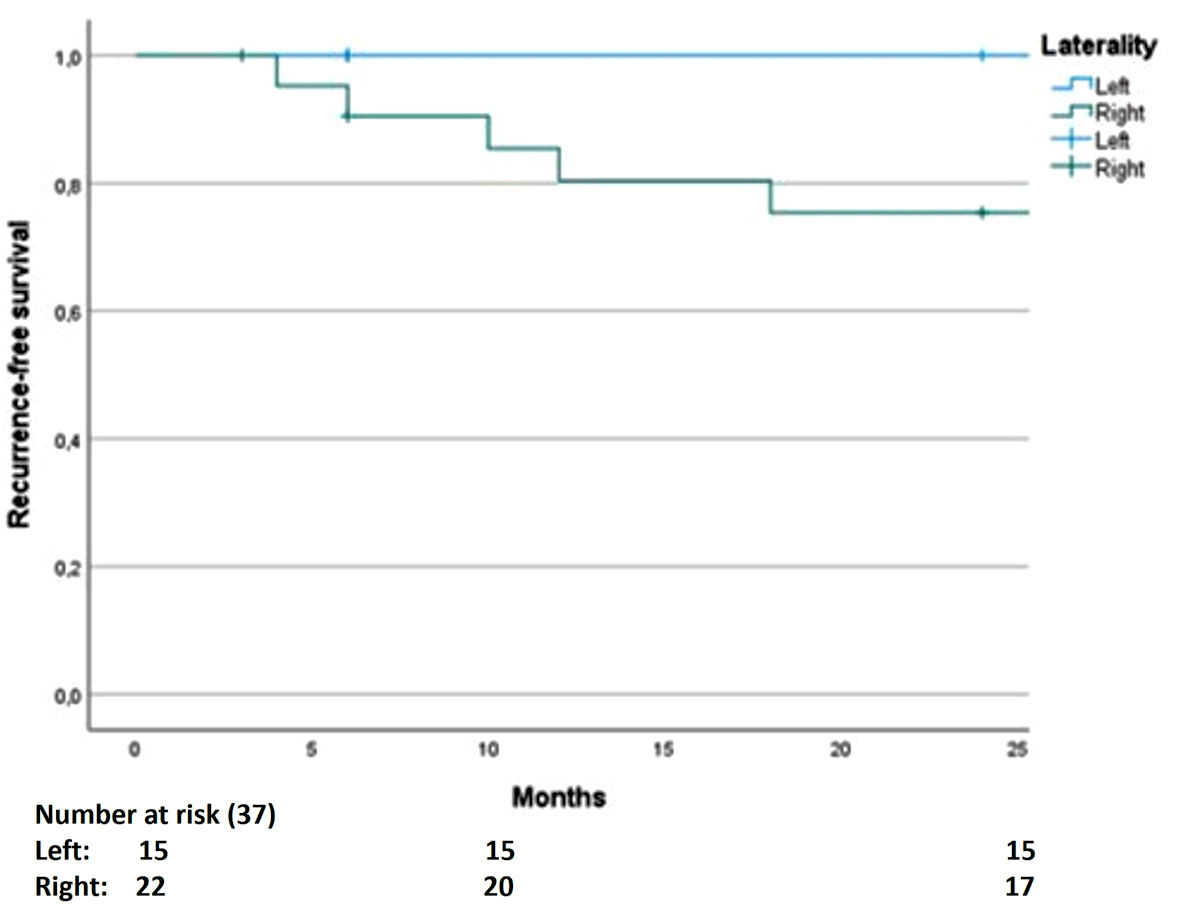 Click for large image | Figure 1. The recurrence-free survival as the primary outcome shows a higher risk in the right-side testicular germ cell tumors. |
We perform an analysis to determine if the size or nodal status were a confounding factor. We found that smaller tumors had more recurrence risk but the difference in size (≥ 3 cm vs. < 3 cm) was no significant (P = 0.581). The nodal status did not modify the primary outcome, the difference between nodal status (positive vs. negative) was non-significant (P = 0.685).
Regarding the secondary outcomes, we observed a higher RFS rate for seminomas (86%) than non-seminomas (83%), although this difference was not statistically significant (Fig. 2). For PFS by laterality, the result was not statistically significant; however, a tendency for higher PFS rate was observed for right tumors (91%) than left tumors (80%), while the PFS rate was 86.5% for the entire cohort (Fig. 3). The 2-year OS rate was 94.5% (two deaths in total, one due to surgical complications after retroperitoneal lymphadenectomy and the other associated with pulmonary metastases).
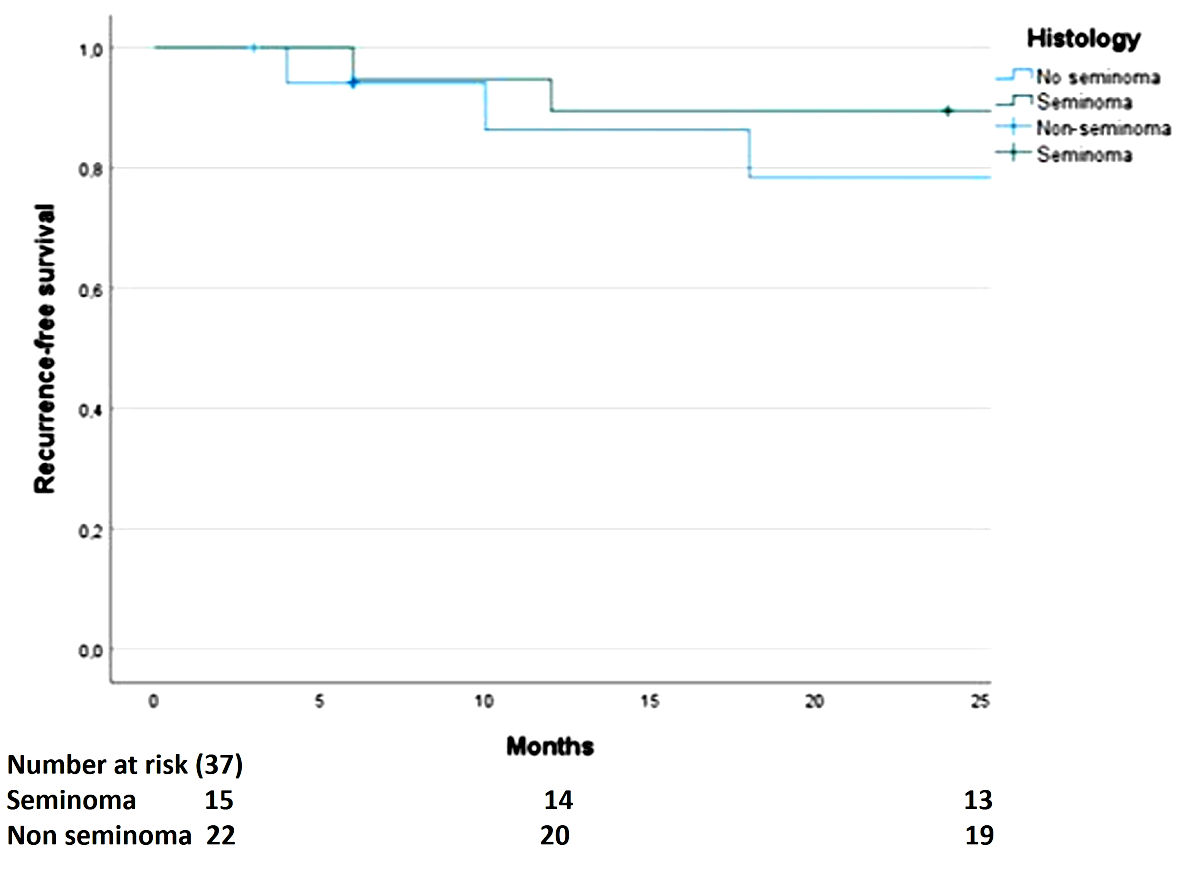 Click for large image | Figure 2. The difference in recurrence-free survival by histology is not significant. |
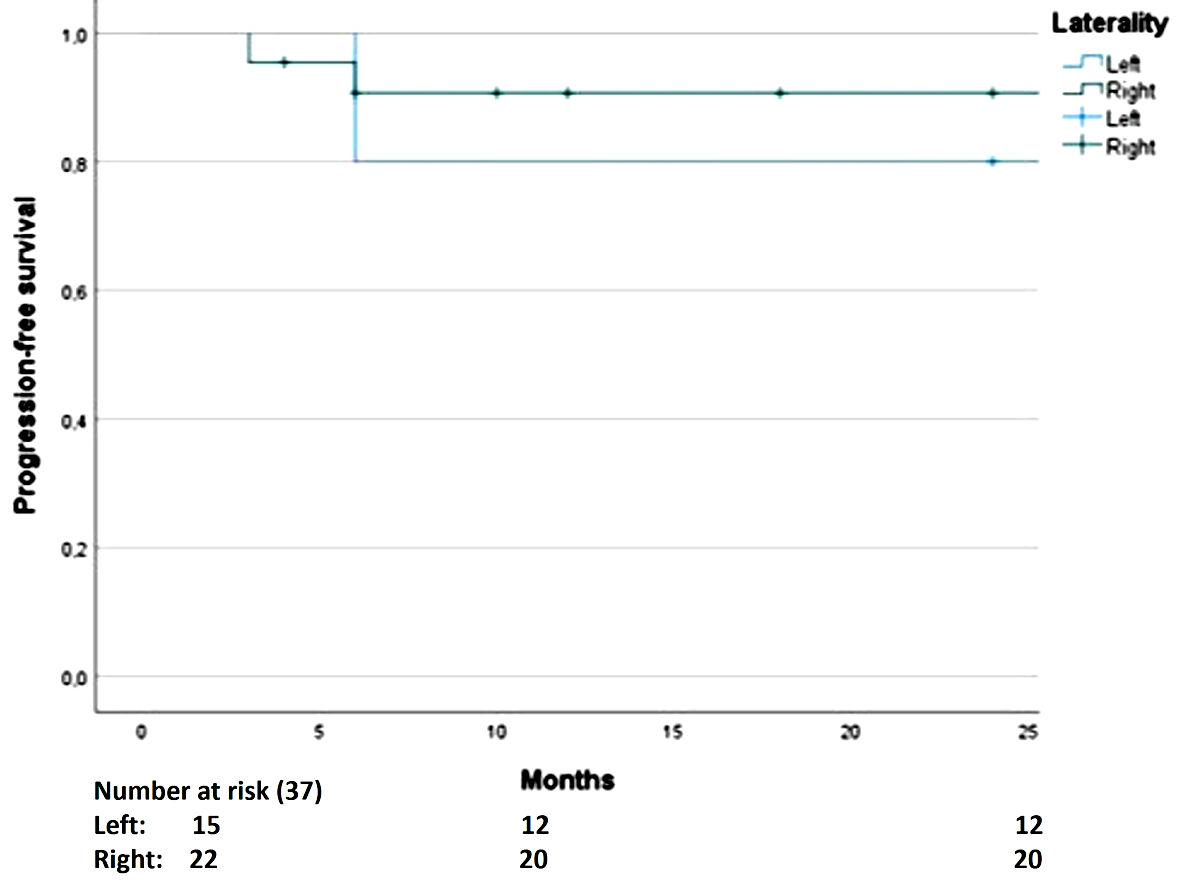 Click for large image | Figure 3. The difference in progression-free survival is not significant. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
The primary outcome of this study shows a trend toward statistical significance, indicating that primary germ cell tumors of the right testis present a higher risk of early recurrence, mainly in the retroperitoneum. The RFS rate at 2 years was 86.5%, being 100% and 77.3% for tumors of the left and right testes, respectively. To date, the impact of tumor laterality on relapses is unknown. Our study may be the basis for performing a study with a larger population to confirm the prognostic value of tumor laterality for relapses.
The lymphatic dissemination in the retroperitoneum for testicular germ cell tumors is predictable. Typically, tumors originating from the right testicle mainly involve the interaortocaval nodes, while those originating from the left testicle involve the para-aortic nodes [3].
Although the mentioned lymphatic drainage pattern is the most frequent pattern according to laterality, there are other known patterns. In right tumors, the first level is the interaortocaval region followed by the precaval and preaortic lymph nodes. In left tumors, the first level is the para-aortic nodes, followed by the preaortic nodes, and finally the interaortocaval nodes [5].
With respect to the size, we used the cutoff of 3 cm according with AJCC the eighth in seminomas; this risk factor for recurrence was analyzed in stage I seminomas but the cutoff was different, Tandstad et al in the Swedish and Norwegian Testicular Cancer Group (SWENOTECA) study used a 4 cm cutoff finding a major risk of recurrence in tumor > 4 cm with a hazard ratio (HR) of 2.7 [6].
Another confounding factor that we ruled out was the nodal status, even with stage II or III our result was not modified. One of the explanations of this result is the use of chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or retroperitoneal lymph node dissection in these stages. The result in our analysis is interesting and supports the laterality as an additional risk factor for recurrence.
Regarding RFS rate by histology, our findings are similar to those reported by the SWENOTECA study in the case of non-seminomas, with RFS rates of 83% and 85%, respectively [7]. However, in the case of seminomas, we found a slightly lower RFS rate than that reported by SWENOTECA (89% vs. 93%) [6]. Notably, these two large SWENOTECA cohorts only included stage I tumors, which could explain the variation from our findings.
Regarding OS, we only have short-term findings, including OS rates of 100% at 2 years in stage I and 94.5% for the entire cohort. Furthermore, no comparative result is available because other studies have reported OS at 5 years; thus, a longer follow-up is necessary for comparative analysis.
The strengths of this study include that it is the first study that reports laterality as a prognostic factor for recurrence in the Mexican population, and it may even be the first such study worldwide because no information was found in the PubMed or Cochrane databases. In addition, the study has an acceptable number of patients at a single center and was carried out in a private center, which specializes in oncological diseases and in which active surveillance and follow-up can be performed according to the international guidelines as we could rule out the size as nodal status as confounding factors.
The main limitation of this study was the methodology. This is a retrospective single-center study that included all stages of the disease in the cohort. Nevertheless, we believe that our study may be the basis for performing a larger analysis and involving more institutions to determine whether tumor laterality can be considered a risk factor for early recurrence with an impact on adjuvant stage I treatment. In this primary analysis, we could not determine the cancer-specific survival because the follow-up time is short.
In conclusion, we found that patients with primary germ cell tumors of the right testicle have a higher risk of recurrence than those with primary germ cell tumors of the left testicle, with a trend toward statistical significance.
Acknowledgments
None to declare.
Financial Disclosure
None to declare.
Conflict of Interest
DMK has provided principal investigator of clinical trials, advisory and speaker services to AstraZeneca, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Roche and Bristol-Myers Squibb. JMRM has provided advisory and speaker services to Ipsen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme and Novartis and received sponsorship for travel and expenses from Bayer. RDH has provided advisory services to Merck Sharp & Dohme and received sponsorship for travel and expenses from Roche. The rest of authors declare no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Author Contributions
The principal author David Davila Dupont collected the data, generated the protocol, contributed to the result’s analysis and contributed in discussion. Daniel Motola Kuba, Thalia de los Milagros Alcantara Velarde and Erika Adriana Martinez Castanada participated in the information search and contributed in the discussion. Rita Dorantes Heredia was the pathologist reviewer. Jose Manuel Ruiz Morales was the reviewer of this paper and contributed in the result’s analysis and the conclusion.
Data Availability
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Abbreviations
OS: overall survival; PFS: progression-free survival; RFS: recurrence-free survival; SWENOTECA: the Swedish and Norwegian Testicular Cancer Group; TGCT: testicular germ cell tumor
| References | ▴Top |
- Batool A, Karimi N, Wu XN, Chen SR, Liu YX. Testicular germ cell tumor: a comprehensive review. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(9):1713-1727.
doi pubmed - Bosl GJ, Motzer RJ. Testicular germ-cell cancer. N Engl J Med. 1997;337(4):242-253.
doi pubmed - Hale GR, Teplitsky S, Truong H, Gold SA, Bloom JB, Agarwal PK. Lymph node imaging in testicular cancer. Transl Androl Urol. 2018;7(5):864-874.
doi pubmed - Stone JM, Cruickshank DG, Sandeman TF, Matthews JP. Laterality, maldescent, trauma and other clinical factors in the epidemiology of testis cancer in Victoria, Australia. Br J Cancer. 1991;64(1):132-138.
doi pubmed - Kreydin EI, Barrisford GW, Feldman AS, Preston MA. Testicular cancer: what the radiologist needs to know. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200(6):1215-1225.
doi pubmed - Tandstad T, Stahl O, Dahl O, Haugnes HS, Hakansson U, Karlsdottir A, Kjellman A, et al. Treatment of stage I seminoma, with one course of adjuvant carboplatin or surveillance, risk-adapted recommendations implementing patient autonomy: a report from the Swedish and Norwegian Testicular Cancer Group (SWENOTECA). Ann Oncol. 2016;27(7):1299-1304.
doi pubmed - Tandstad T, Dahl O, Cohn-Cedermark G, Cavallin-Stahl E, Stierner U, Solberg A, Langberg C, et al. Risk-adapted treatment in clinical stage I nonseminomatous germ cell testicular cancer: the SWENOTECA management program. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(13):2122-2128.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
World Journal of Oncology is published by Elmer Press Inc.


